Inflammatory monocyte recruitment is regulated by interleukin-23 during systemic bacterial infection
- PMID: 22966045
- PMCID: PMC3497429
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00589-12
Inflammatory monocyte recruitment is regulated by interleukin-23 during systemic bacterial infection
Abstract
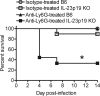
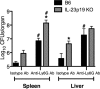
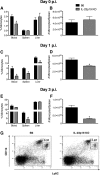
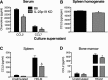
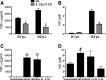
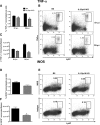
Listeria monocytogenes is a gram-positive intracellular pathogen that causes meningitis and septicemia in immunocompromised individuals and spontaneous abortion in pregnant women. The innate immune response against L. monocytogenes is primarily mediated by neutrophils and monocytes. Interleukin-23 (IL-23) is an important proinflammatory cytokine well known for its role in neutrophil recruitment in various infectious and autoimmune diseases. We have previously shown that IL-23 is required for host resistance against L. monocytogenes and for neutrophil recruitment to the liver, but not the spleen, during infection. Despite efficient neutrophil recruitment to the spleen, IL-23p19 knockout (KO) mice have an increased bacterial burden in this organ, suggesting that IL-23 may regulate the recruitment/function of another cell type to the spleen. In this study, we show that specific depletion of neutrophils abrogated the differences in bacterial burdens in the livers but not the spleens of C57BL/6 (B6) and IL-23p19 KO mice. Interestingly, L. monocytogenes-infected IL-23p19 KO mice had fewer monocytes in the spleen than B6 mice, as well as a reduction in the monocyte-recruiting chemokines CCL2 and CCL7. Additionally, the overall concentrations of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and nitric oxide (NO(•)), as well as the percentages and total numbers of monocytes producing TNF-α and NO(•), were reduced in IL-23p19 KO mice compared to levels in B6 mice, leading to increased bacterial burdens in the spleens of L. monocytogenes-infected IL-23p19 KO mice. Collectively, our data establish that IL-23 is required for the optimal recruitment of TNF-α- and NO(•)-producing inflammatory monocytes, thus revealing a novel mechanism by which this proinflammatory cytokine provides protection against bacterial infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-23 is required for protection against systemic infection with Listeria monocytogenes.J Immunol. 2009 Dec 15;183(12):8026-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901588. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19923464
-
Toxoplasma gondii profilin promotes recruitment of Ly6Chi CCR2+ inflammatory monocytes that can confer resistance to bacterial infection.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Jun 12;10(6):e1004203. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004203. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24945711 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophils Are More Effective than Monocytes at Phagosomal Containment and Killing of Listeria monocytogenes.Immunohorizons. 2019 Dec 13;3(12):573-584. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.1900065. Immunohorizons. 2019. PMID: 31836639
-
Monocyte-mediated immune defense against murine Listeria monocytogenes infection.Adv Immunol. 2012;113:119-34. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394590-7.00003-8. Adv Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22244581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monocyte trafficking in acute and chronic inflammation.Trends Immunol. 2011 Oct;32(10):470-7. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.05.001. Epub 2011 Jun 12. Trends Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21664185 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-36 Cytokine/Receptor Signaling: A New Target for Tissue Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 4;21(18):6458. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186458. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32899668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low frequency, weak MCP-1 secretion and exhausted immune status of peripheral monocytes were associated with progression of severe enterovirus A71-infected hand, foot and mouth disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2019 Jun;196(3):353-363. doi: 10.1111/cei.13267. Epub 2019 Feb 17. Clin Exp Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30697697 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the Regulatory Mechanisms by Which NLRX1 Modulates Innate Immune Responses to Helicobacter pylori Infection.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 14;10(9):e0137839. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137839. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26367386 Free PMC article.
-
Fasting metabolism modulates the interleukin-12/interleukin-10 cytokine axis.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 24;12(7):e0180900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180900. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28742108 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Hidden Regulators: The Impact of lncRNAs on Zoonoses.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 21;25(6):3539. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063539. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542512 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bonello GB, et al. 2011. An evolutionarily conserved TNF-alpha-responsive enhancer in the far upstream region of human CCL2 locus influences its gene expression. J. Immunol. 186:7025–7038 - PubMed
-
- Boring L, Gosling J, Cleary M, Charo IF. 1998. Decreased lesion formation in CCR2−/− mice reveals a role for chemokines in the initiation of atherosclerosis. Nature 394:894–897 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

