Elevated serum interleukin-10 at time of hospital admission is predictive of mortality in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia
- PMID: 22966128
- PMCID: PMC6281403
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jis552
Elevated serum interleukin-10 at time of hospital admission is predictive of mortality in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia (SaB) carries considerable morbidity and mortality. We examined the predictive value of serum concentrations of interleukin (IL)-10, proinflammatory cytokines, and terminal complement on patient survival and SaB duration.
Methods: Clinical information on consecutive patients with SaB at a tertiary medical center were collected prospectively. Patient serum samples obtained at the day of clinical presentation were assayed for tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-1β, IL-10, and complement membrane attack complex C5b-9 concentrations using enzyme-linked immunoassay. Logistic regression identified predictors of mortality and duration of bacteremia.
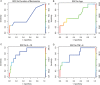
Results: In 59 patients with SaB, 14% died and 17% had prolonged bacteremia (>4 days). Elevated IL-10 serum concentrations (>7.8 pg/mL) identified all 8 patients who died, whereas there were no deaths in patients with normal IL-10 (P = .016). The lack of an IL-1β response (≤0.45 pg/mL) defined all patients with SaB >4 days. In multivariate analysis, patient age (odds ratio [OR], 1.16; P = .022), duration of bacteremia (OR, 1.16; P = .031), and serum IL-10 (OR, 1.05; P = .014) were identified as independent predictors of patient mortality.
Conclusions: SaB mortality was confined strictly to patients with elevated IL-10 concentrations. We recommend that future clinical trials of SaB stratify patients according to IL-10 and IL-1β serum concentrations in order to better evaluate the impact of therapeutic interventions on patient outcome.
Figures
References
-
- van Dissel JT, van Langevelde P, Westendorp RG, Kwappenberg K, Frolich M. Anti-inflammatory cytokine profile and mortality in febrile patients. Lancet. 1998;351:950–3. - PubMed
-
- Chau TA, McCully ML, Brintnell W, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 ligands on the staphylococcal cell wall downregulate superantigen-induced T cell activation and prevent toxic shock syndrome. Nat Med. 2009;15:641–8. - PubMed
-
- Frodermann V, Chau TA, Sayedyahossein S, Toth JM, Heinrichs DE, Madrenas J. A modulatory interleukin-10 response to staphylococcal peptidoglycan prevents Th1/Th17 adaptive immunity to Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 2011;204:253–62. - PubMed