Decreased birth weight in psychosis: influence of prenatal exposure to serologically determined influenza and hypoxia
- PMID: 22966148
- PMCID: PMC3756769
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbs084
Decreased birth weight in psychosis: influence of prenatal exposure to serologically determined influenza and hypoxia
Abstract
Background: Decreased birth weight (BW) is associated with later psychosis, but the sources of decreased BW for those at risk for psychosis remain unclear.
Aim: To determine whether fetal exposure to influenza and/or hypoxia accounts for BW decreases among psychotic cases and controls.
Method: Subjects were 111 cases diagnosed with schizophrenia or affective psychosis and 333 matched controls from the Collaborative Perinatal Project. Psychiatric diagnoses were ascertained from medical records. Influenza and hypoxia were determined from maternal and cord sera collected at birth.
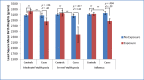
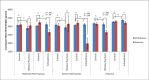
Results: Cases exposed to severe fetal hypoxia or influenza had significantly lower BW compared with unexposed cases and controls, regardless of exposure status. No significant differences in BW were observed among controls based on exposure status.
Conclusions: Decreased BW appears to be a risk factor for psychosis only in the presence of other teratogens. Liability to psychosis likely renders fetuses vulnerable to decreased fetal growth in response to hypoxia and influenza.
Keywords: obstetric complications; pregnancy; schizophrenia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decreased neurotrophic response to birth hypoxia in the etiology of schizophrenia.Biol Psychiatry. 2008 Nov 1;64(9):797-802. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.04.012. Epub 2008 May 16. Biol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18486103 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective cohort study of genetic and perinatal influences in the etiology of schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull. 2000;26(2):351-66. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.schbul.a033458. Schizophr Bull. 2000. PMID: 10885636
-
Cognitive functioning prior to the onset of psychosis: the role of fetal exposure to serologically determined influenza infection.Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Jun 15;65(12):1040-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.12.015. Epub 2009 Feb 5. Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19195645 Free PMC article.
-
[Obstetrical complications and further schizophrenia of the infant: a new medicolegal threat to the obstetrician?].J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2003 Dec;32(8 Pt 1):720-7. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2003. PMID: 15067896 Review. French.
-
Obstetric complications and schizophrenia: prenatal underdevelopment and subsequent neurodevelopmental impairment.Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 2001 Apr;40:s25-9. doi: 10.1192/bjp.178.40.s25. Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 2001. PMID: 11315220 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of environmental factors in severe psychiatric disorders.Front Neurosci. 2014 Feb 11;8:19. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00019. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24574956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal cortisol during pregnancy and offspring schizophrenia: Influence of fetal sex and timing of exposure.Schizophr Res. 2019 Nov;213:15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2019.07.002. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Schizophr Res. 2019. PMID: 31345704 Free PMC article.
-
Pursuit of the "truth" about mental illness: the significance of findings in neuropsychiatric research, and lessons from the past.Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2014 Dec;16(4):447-50. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2014.16.4/ldelisi. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25733950 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental Risk Factors and Cognitive Outcomes in Psychosis: Pre-, Perinatal, and Early Life Adversity.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2023;63:205-240. doi: 10.1007/7854_2022_378. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 35915384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymorphisms in the hypoxia inducible factor binding site of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor gene promoter in schizophrenia.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 24;17(3):e0265738. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265738. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35324982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kunugi H, Nanko S, Murray RM. Obstetric complications and schizophrenia: prenatal underdevelopment and subsequent neurodevelopmental impairment. Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 2001;40:s25––s29 - PubMed
-
- Lane EA, Albee GW. Comparative birth weights of schizophrenics and their siblings. J Psychol. 1966;64:227––231
-
- Abel KM, Wicks S, Susser ES, et al. Birth weight, schizophrenia, and adult mental disorder: is risk confined to the smallest babies? Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:923––930 - PubMed
-
- Cannon TD, Rosso IM, Hollister JM, Bearden CE, Sanchez LE, Hadley T. A prospective cohort study of genetic and perinatal influences in the etiology of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2000;26:351––366 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

