Requirement for SNAPC1 in transcriptional responsiveness to diverse extracellular signals
- PMID: 22966203
- PMCID: PMC3486178
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00906-12
Requirement for SNAPC1 in transcriptional responsiveness to diverse extracellular signals
Abstract
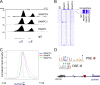
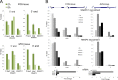
Initiation of transcription of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII)-dependent genes requires the participation of a host of basal transcription factors. Among genes requiring RNAPII for transcription, small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) display a further requirement for a factor known as snRNA-activating protein complex (SNAPc). The scope of the biological function of SNAPc and its requirement for transcription of protein-coding genes has not been elucidated. To determine the genome-wide occupancy of SNAPc, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by high-throughput sequencing using antibodies against SNAPC4 and SNAPC1 subunits. Interestingly, while SNAPC4 occupancy was limited to snRNA genes, SNAPC1 chromatin residence extended beyond snRNA genes to include a large number of transcriptionally active protein-coding genes. Notably, SNAPC1 occupancy on highly active genes mirrored that of elongating RNAPII extending through the bodies and 3' ends of protein-coding genes. Inhibition of transcriptional elongation resulted in the loss of SNAPC1 from the 3' ends of genes, reflecting a functional association between SNAPC1 and elongating RNAPII. Importantly, while depletion of SNAPC1 had a small effect on basal transcription, it diminished the transcriptional responsiveness of a large number of genes to two distinct extracellular stimuli, epidermal growth factor (EGF) and retinoic acid (RA). These results highlight a role for SNAPC1 as a general transcriptional coactivator that functions through elongating RNAPII.
Figures





References
-
- Amit I, et al. 2007. A module of negative feedback regulators defines growth factor signaling. Nat. Genet. 39:503–512 - PubMed
-
- Cesaroni M, Cittaro D, Brozzi A, Pelicci PG, Luzi L. 2008. CARPET: a web-based package for the analysis of ChIP-chip and expression tiling data. Bioinformatics 24:2918–2920 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
