Pathologies Associated with Serum IgG4 Elevation
- PMID: 22966232
- PMCID: PMC3433130
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/602809
Pathologies Associated with Serum IgG4 Elevation
Abstract
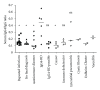
Statement of Purpose. IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is usually associated to an increase of serum IgG4 levels. However other conditions have also been associated to high serum IgG4 levels. Methods. All IgG subclasses analyses performed in our hospital over a one-year period were analyzed. When IgG4 level were over 1.35 g/L, the patient's clinical observation was analyzed and both final diagnosis and reason leading to IgG subclasses analysis were recorded. Only polyclonal increases of IgG4 were considered. Summary of the Results. On 646 IgG subclass analysis performed, 59 patients had serum IgG4 over 1.35 g/L. The final diagnosis associated to serum IgG4 increase was very variable. Most patients (25%) presented with repeated infections, 13.5% with autoimmune diseases, and 10% with IgG4-RD. Other patients presented with cancer, primary immune deficiencies, idiopathic interstitial lung disease, cystic fibrosis, histiocytosis, or systemic vasculitis and 13.5% presented with various pathologies or no diagnosis. Mean IgG4 levels and IgG4/IgG ratio were higher in IgG4-RD than in other pathologies associated to elevated IgG4 levels. Conclusions. Our study confirms that elevation of serum IgG4 is not specific to IgG4-RD. Before retaining IgG4-RD diagnosis in cases of serum IgG4 above 1.35 g/L, several other pathological conditions should be excluded.
Figures

References
-
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2001;344(10):732–738. - PubMed
-
- Aalberse RC, Van Milligen F, Tan KY, Stapel SO. Allergen-specific IgG4 in atopic disease. Allergy. 1993;48(8):559–569. - PubMed
-
- Hussain R, Poindexter RW, Ottesen EA. Control of allergic reactivity in human filariasis: predominant localization of blocking antibody to the IgG4 subclass. Journal of Immunology. 1992;148(9):2731–2737. - PubMed
-
- Shirakata Y, Shiraishi S, Sayama K, Miki Y. Subclass characteristics of IgG autoantibodies in bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus. Journal of Dermatology. 1990;17(11):661–666. - PubMed
-
- Sarles H, Sarles JC, Muratore R, Guien C. Chronic inflammatory sclerosis of the pancreas—an autonomous pancreatic disease? The American Journal of Digestive Diseases. 1961;6(7):688–698. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

