Restoration of innate and adaptive immune responses by HCV viral inhibition with an induction approach using natural interferon-beta in chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 22966239
- PMCID: PMC3433154
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/582716
Restoration of innate and adaptive immune responses by HCV viral inhibition with an induction approach using natural interferon-beta in chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
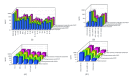
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) is a serious medical problem necessitating more effective treatment. This study investigated the hypothesis that an induction approach with nIFN-beta for 24 weeks followed by PEG-IFN-alpha+ribavirin (standard of care: SOC) for 48 weeks (novel combination treatment: NCT) would increase the initial virologic response rate and restore innate and adaptive immune responses in CHC. Seven CHC patients with a high viral load and genotype 1b were treated with NCT. Serum cytokine and chemokine levels were evaluated during NCT. NCT prevented viral escape and breakthrough resulting in persistent viral clearance of HCVRNA. IL-15 was increased at the end of induction therapy in both early virologic responders (EAVRs) and late virologic responders (LAVRs); CXCL-8, CXCL-10, and CCL-4 levels were significantly decreased (P < 0.05) in EAVR but not in LAVR during NCT, and IL-12 increased significantly (P < 0.05) and CXCL-8 decreased significantly (P < 0.05) after the end of NCT in EAVR but not in LAVR. NCT prevented viral breakthrough with viral clearance leading to improvement of innate and adaptive immunity resulting in a sustained virologic response (SVR). NCT (n = 8) achieved a higher SVR rate than SOC (n = 8) in difficult-to-treat CHC patients with genotype 1 and high viral loads.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Multiple cytokine profiling of the therapeutic responses to ribavirin and pegylated interferon-alpha2b using an "induction" approach with natural interferon-beta in difficult-to-treat chronic hepatitis C.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009 Jun;29(6):353-68. doi: 10.1089/jir.2008.0110. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009. PMID: 19441887
-
Lead-in treatment with interferon-β/ribavirin may modify the early hepatitis C virus dynamics in pegylated interferon alpha-2b/ribavirin combination for chronic hepatitis C patients with the IL28B minor genotype.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Mar;28(3):443-9. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12039. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23173698 Clinical Trial.
-
[Efficacy and safety of pegylated interferon α-2b injection (Y shape, 40 kD) in treatment of patients with genotype 1/6 chronic hepatitis C].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2017 Mar 20;25(3):187-194. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.03.006. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28482405 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Hepatitis C: viral and host factors associated with non-response to pegylated interferon plus ribavirin.Liver Int. 2010 Oct;30(9):1259-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2010.02283.x. Liver Int. 2010. PMID: 20633102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase III results of Boceprevir in treatment naïve patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1.Liver Int. 2012 Feb;32 Suppl 1:27-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02725.x. Liver Int. 2012. PMID: 22212568 Review.
Cited by
-
A Protease Inhibitor with Induction Therapy with Natural Interferon-β in Patients with HCV Genotype 1b Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Mar 9;17(3):350. doi: 10.3390/ijms17030350. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27005617 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Shepard CW, Finelli L, Alter MJ. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2005;5(9):558–567. - PubMed
-
- Seeff LB. Natural history of chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002;36(5):S35–S46. - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of hepatitis C virus infection. Journal of Hepatology. 2011;55(2):245–264. - PubMed
-
- McHutchison JG, Everson GT, Gordon SC, et al. Telaprevir with peginterferon and ribavirin for chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. New England Journal of Medicine. 2009;360(18):1827–1838. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

