Gene expression profile reveals abnormalities of multiple signaling pathways in mesenchymal stem cell derived from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 22966240
- PMCID: PMC3433142
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/826182
Gene expression profile reveals abnormalities of multiple signaling pathways in mesenchymal stem cell derived from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
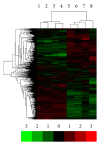
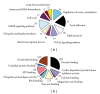
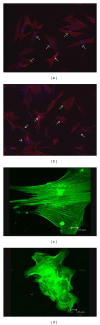
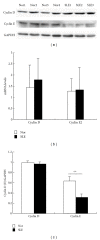
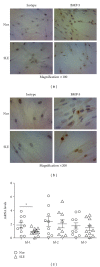
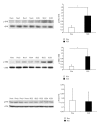
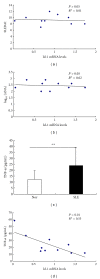
We aimed to compare bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMMSCs) between systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and normal controls by means of cDNA microarray, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and immunoblotting. Our results showed there were a total of 1, 905 genes which were differentially expressed by BMMSCs derived from SLE patients, of which, 652 genes were upregulated and 1, 253 were downregulated. Gene ontology (GO) analysis showed that the majority of these genes were related to cell cycle and protein binding. Pathway analysis exhibited that differentially regulated signal pathways involved actin cytoskeleton, focal adhesion, tight junction, and TGF-β pathway. The high protein level of BMP-5 and low expression of Id-1 indicated that there might be dysregulation in BMP/TGF-β signaling pathway. The expression of Id-1 in SLE BMMSCs was reversely correlated with serum TNF-α levels. The protein level of cyclin E decreased in the cell cycling regulation pathway. Moreover, the MAPK signaling pathway was activated in BMMSCs from SLE patients via phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and SAPK/JNK. The actin distribution pattern of BMMSCs from SLE patients was also found disordered. Our results suggested that there were distinguished differences of BMMSCs between SLE patients and normal controls.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activated NF-κB in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients inhibits osteogenic differentiation through downregulating Smad signaling.Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Feb 15;22(4):668-78. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0226. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 22897816 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Galectin-1-producing mesenchymal stem cells restrain the proliferation of T lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2024 Oct;46(5):618-626. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2024.2384913. Epub 2024 Aug 4. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2024. PMID: 39099224
-
Upregulation of p16INK4A promotes cellular senescence of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients.Cell Signal. 2012 Dec;24(12):2307-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.07.012. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 22820504
-
LncRNA H19 induces immune dysregulation of BMMSCs, at least partly, by inhibiting IL-2 production.Mol Med. 2021 Jun 15;27(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00326-y. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34130625 Free PMC article.
-
JAK-STAT signaling mediates the senescence of bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2017 Mar 1;49(3):208-215. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmw134. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2017. PMID: 28177455
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Derived From Crohn's Patients Deploy Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated Immune Suppression, Independent of Autophagy.Mol Ther. 2015 Jul;23(7):1248-1261. doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.67. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Mol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25899824 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Homeostasis and Systemic Diseases: Hypothesis, Evidences, and Therapeutic Opportunities.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 31;20(15):3738. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153738. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31370159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reevaluation of Pluripotent Cytokine TGF-β3 in Immunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 1;19(8):2261. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082261. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30071700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic contribution to mesenchymal stem cell dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 May 24;9(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0898-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29793537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates secondary osteoporosis through interleukin-17-impaired functions of recipient bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in MRL/lpr mice.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 May 27;6(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0091-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26012584 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Isenberg DA, Rahman A. Systemic lupus erythematosus. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2008;358(9):929–939. - PubMed
-
- Ikehara S, Inaba M, Yasumizu R, et al. Autoimmune diseases as stem cell disorders. Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine. 1994;173(1):141–155. - PubMed
-
- Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997;276(5309):71–74. - PubMed
-
- Noort WA, Kruisselbrink AB, In’t Anker PS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote engraftment of human umbilical cord blood-derived CD34+ cells in NOD/SCID mice. Experimental Hematology. 2002;30(8):870–878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

