Effect of thalidomide and arsenic trioxide on the release of tumor necrosis factor-α and vascular endothelial growth factor from the KG-1a human acute myelogenous leukemia cell line
- PMID: 22966360
- PMCID: PMC3436389
- DOI: 10.3892/ol_00000116
Effect of thalidomide and arsenic trioxide on the release of tumor necrosis factor-α and vascular endothelial growth factor from the KG-1a human acute myelogenous leukemia cell line
Abstract
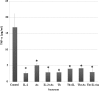
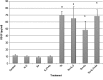
Studies conducted in our lab have indicated that thalidomide cytotoxicity in the KG-1a human acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) cell line was enhanced by combining it with arsenic trioxide. The current investigation was conducted in order to evaluate the effect of thalidomide either alone or in combination with arsenic trioxide on the release of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from this cell line in an attempt to clarify its possible cytotoxic mechanism(s). Human AML cell line KG-1a was used in this study. The cells were cultured for 48 h in the presence or absence of thalidomide (5 mg/l), and or arsenic trioxide (4 μM). The levels of TNF-α and VEGF in the supernatant were determined by ELISA. Results obtained indicate that the levels of TNF-α in the supernatant of KG-1a cell cultures incubated with thalidomide, arsenic trioxide, or combination were statistically lower than those observed in the supernatant of control cells (2.89, 5.07, 4.15 and 16.88 pg/ml, respectively). However, the levels of VEGF in the supernatant of thalidomide-treated cells were statistically higher than those in the supernatant of control cells (69.61 vs. 11.48 pg/l). Arsenic trioxide, whether alone or in combination with thalidomide, did not produce any statistically significant difference in the levels of VEGF as compared to the control or thalidomide-treated cell supernatant. These findings indicate that thalidomide and the arsenic trioxide inhibition of TNF-α production by KG-1a cells may play an important role in their cytotoxic effect.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arsenic trioxide enhances the cytotoxic effect of thalidomide in a KG-1a human acute mylogenous leukemia cell line.Oncol Lett. 2010 May;1(3):473-479. doi: 10.3892/ol_00000083. Oncol Lett. 2010. PMID: 21442015 Free PMC article.
-
[Experimental study of the anti-tumor effect of arsenic trioxide or thalidomide alone and combination of both for treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome model].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Mar;44(3):228-33. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16624066 Chinese.
-
Therapeutic and prophylactic thalidomide in TNBS-induced colitis: synergistic effects on TNF-alpha, IL-12 and VEGF production.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Apr 21;13(15):2166-73. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i15.2166. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17465495 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition factors of arsenic trioxide therapeutic effects in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia.Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(19):3503-6. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014. PMID: 25269921 Review.
-
[Angiogenesis in patients with hematologic malignancies].Onkologie. 2001 Sep;24 Suppl 5:75-80. doi: 10.1159/000055192. Onkologie. 2001. PMID: 11600818 Review. German.
References
-
- McGeehan GM, Uhl J. TNF-α in human diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 1996;2:662–667.
-
- Girardin E, Grau GE, Dayer JM, Roux-Lombard P, Lambert PH. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in the serum of children with severe infectious purpura. N Eng J Med. 1988;319:397–400. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
