Weekly pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and paclitaxel in patients with metastatic breast carcinoma: A phase II study
- PMID: 22966374
- PMCID: PMC3436426
- DOI: 10.3892/ol_00000131
Weekly pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and paclitaxel in patients with metastatic breast carcinoma: A phase II study
Abstract
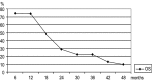
Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) has the advantage of delivering active anthracycline directly to the tumor site, while exposing the patient to a lesser degree of doxorubicin-associated toxicities. Recently, a regimen in which paclitaxel is infused weekly over 1 h produced substantial antitumor activity with little myelosuppression. We designed a phase II trial to study the efficacy and toxicity of 10 mg/m(2) PLD on Days 1, 8 and 15, plus 70 mg/m(2) paclitaxel weekly in patients with untreated metastatic breast cancer and a high risk of cardiotoxicity. The study included 35 patients, with 31 (88.5%) evaluable for efficacy and 35 (100%) for toxicity. A total of 28 patients (80%) had two or more sites of disease. Overall, 4 complete and 16 partial responses were noted with an overall response rate of 64.5%, with 6 cases of stable and 5 cases of progressive disease. Toxicity was found to be manageable in that the only grade 3-4 side effects recorded were palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, 8.5%; mucositis, 2.8%; leucopenia, 12.5%; anemia, 2.8% and AST/ALT, 2.8%. No cardiotoxicity was observed. In conclusion, weekly PLD plus paclitaxel appears to be a well-tolerated and effective approach for metastatic breast cancer patients with a high risk of cardiotoxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialist Group (EBCTCG) Effect of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomized trials. Lancet. 2005;365:1687–1717. - PubMed
-
- Hortobagyi GN. Anthracyclines in the treatment of cancer: an overview. Drugs. 1997;54(Suppl 4):1–7. - PubMed
-
- Von Hoff D, Layard M, Basa P, Davcis HL, von Hoff AL, Rozencweig M, Muggia FM. Risk factors for doxorubicin-induced congestive heart failure. Ann Inter Med. 1979;91:710–717. - PubMed
-
- Swain S, Whaley FS, Ewer MS. Congestive heart failure in patients treated with doxorubicin: a retrospective analysis of three trials. Cancer. 2003;97:2869–2879. - PubMed
-
- Pai VB, Nahata MC. Cardiotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents: incidence, treatment and prevention. Drug Saf. 2000;22:263–302. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources