Riluzole-triggered GSH synthesis via activation of glutamate transporters to antagonize methylmercury-induced oxidative stress in rat cerebral cortex
- PMID: 22966415
- PMCID: PMC3432391
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/534705
Riluzole-triggered GSH synthesis via activation of glutamate transporters to antagonize methylmercury-induced oxidative stress in rat cerebral cortex
Abstract
Objective: This study was to evaluate the effect of riluzole on methylmercury- (MeHg-) induced oxidative stress, through promotion of glutathione (GSH) synthesis by activating of glutamate transporters (GluTs) in rat cerebral cortex.
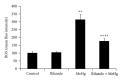
Methods: Eighty rats were randomly assigned to four groups, control group, riluzole alone group, MeHg alone group, and riluzole + MeHg group. The neurotoxicity of MeHg was observed by measuring mercury (Hg) absorption, pathological changes, and cell apoptosis of cortex. Oxidative stress was evaluated via determining reactive oxygen species (ROS), 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), malondialdehyde (MDAs), carbonyl, sulfydryl, and GSH in cortex. Glutamate (Glu) transport was studied by measuring Glu, glutamine (Gln), mRNA, and protein of glutamate/aspartate transporter (GLAST) and glutamate transporter-1 (GLT-1).
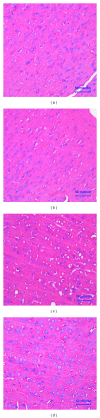
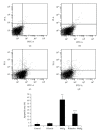
Result: (1) MeHg induced Hg accumulation, pathological injury, and apoptosis of cortex; (2) MeHg increased ROS, 8-OHdG, MDA, and carbonyl, and inhibited sulfydryl and GSH; (3) MeHg elevated Glu, decreased Gln, and downregulated GLAST and GLT-1 mRNA expression and protein levels; (4) riluzole antagonized MeHg-induced downregulation of GLAST and GLT-1 function and expression, GSH depletion, oxidative stress, pathological injury, and apoptosis obviously.
Conclusion: Data indicate that MeHg administration induced oxidative stress in cortex and that riluzole could antagonize this situation through elevation of GSH synthesis by activating of GluTs.
Figures



References
-
- Turner MD, Marsh DO, Smith JC, et al. Methylmercury in populations eating large quantities of marine fish. Archives of Environmental Health. 1980;35(6):367–378. - PubMed
-
- Aschner M, Syversen T, Souza DO, Rocha JBT, Farina M. Involvement of glutamate and reactive oxygen species in methylmercury neurotoxicity. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research. 2007;40(3):285–291. - PubMed
-
- Shanker G, Aschner M. Methylmercury-induced reactive oxygen species formation in neonatal cerebral astrocytic cultures is attenuated by antioxidants. Molecular Brain Research. 2003;110(1):85–91. - PubMed
-
- Yee S, Choi BH. Oxidative stress in neurotoxic effects of methylmercury poisoning. NeuroToxicology. 1996;17(1):17–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

