Integrin αvβ3 and CD44 pathways in metastatic prostate cancer cells support osteoclastogenesis via a Runx2/Smad 5/receptor activator of NF-κB ligand signaling axis
- PMID: 22966907
- PMCID: PMC3499378
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-66
Integrin αvβ3 and CD44 pathways in metastatic prostate cancer cells support osteoclastogenesis via a Runx2/Smad 5/receptor activator of NF-κB ligand signaling axis
Abstract
Background: Bone loss and pathological fractures are common skeletal complications associated with androgen deprivation therapy and bone metastases in prostate cancer patients. We have previously demonstrated that prostate cancer cells secrete receptor activator of NF-kB ligand (RANKL), a protein essential for osteoclast differentiation and activation. However, the mechanism(s) by which RANKL is produced remains to be determined. The objective of this study is to gain insight into the molecular mechanisms controlling RANKL expression in metastatic prostate cancer cells.
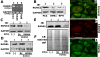
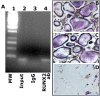
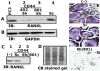
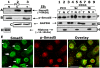
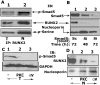
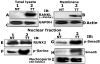
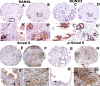
Results: We show here that phosphorylation of Smad 5 by integrin αvβ3 and RUNX2 by CD44 signaling, respectively, regulates RANKL expression in human-derived PC3 prostate cancer cells isolated from bone metastasis. We found that RUNX2 intranuclear targeting is mediated by phosphorylation of Smad 5. Indeed, Smad5 knock-down via RNA interference and inhibition of Smad 5 phosphorylation by an αv inhibitor reduced RUNX2 nuclear localization and RANKL expression. Similarly, knockdown of CD44 or RUNX2 attenuated the expression of RANKL. As a result, conditioned media from these cells failed to support osteoclast differentiation in vitro. Immunohistochemistry analysis of tissue microarray sections containing primary prostatic tumor (grade2-4) detected predominant localization of RUNX2 and phosphorylated Smad 5 in the nuclei. Immunoblotting analyses of nuclear lysates from prostate tumor tissue corroborate these observations.
Conclusions: Collectively, we show that CD44 signaling regulates phosphorylation of RUNX2. Localization of RUNX2 in the nucleus requires phosphorylation of Smad-5 by integrin αvβ3 signaling. Our results suggest possible integration of two different pathways in the expression of RANKL. These observations imply a novel mechanistic insight into the role of these proteins in bone loss associated with bone metastases in patients with prostate cancer.
Figures
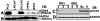
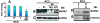

Similar articles
-
DU145 human prostate cancer cells express functional receptor activator of NFkappaB: new insights in the prostate cancer bone metastasis process.Bone. 2007 Apr;40(4):981-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2006.11.006. Epub 2006 Dec 28. Bone. 2007. PMID: 17196895
-
Characterization of CD44 intracellular domain interaction with RUNX2 in PC3 human prostate cancer cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Jul 22;17(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0395-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31331331 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of osteopontin and CD44 as metastatic principles in prostate cancer cells.Mol Cancer. 2007 Mar 7;6:18. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-6-18. Mol Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17343740 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB (RANK) ligand in prostate cancer bone metastases.BJU Int. 2008 May;101(9):1071-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07364.x. Epub 2007 Dec 5. BJU Int. 2008. PMID: 18070191 Review.
-
Regulatory mechanisms of osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation.Oral Dis. 2002 May;8(3):147-59. doi: 10.1034/j.1601-0825.2002.01829.x. Oral Dis. 2002. PMID: 12108759 Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential of Extracellular Matrix- and Integrin Adhesion Complex-Related Molecules for Prostate Cancer Biomarker Discovery.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 28;12(1):79. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010079. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38255186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of sequence-specific interactions of the CD44-intracellular domain with RUNX2 in the transcription of matrix metalloprotease-9 in human prostate cancer cells.Cancer Drug Resist. 2020 3rd Quarter;3(3):586-602. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2020.21. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 33062960 Free PMC article.
-
The Thyroid Hormone Receptor-RUNX2 Axis: A Novel Tumor Suppressive Pathway in Breast Cancer.Horm Cancer. 2020 Feb;11(1):34-41. doi: 10.1007/s12672-019-00373-2. Epub 2019 Dec 21. Horm Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31865591 Free PMC article.
-
The receptor for urokinase-plasminogen activator (uPAR) controls plasticity of cancer cell movement in mesenchymal and amoeboid migration style.Oncotarget. 2014 Mar 30;5(6):1538-53. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1754. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24681666 Free PMC article.
-
A Potential Role of RUNX2- RUNT Domain in Modulating the Expression of Genes Involved in Bone Metastases: An In Vitro Study with Melanoma Cells.Cells. 2020 Mar 19;9(3):751. doi: 10.3390/cells9030751. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32204402 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

