Trends in the treatment of adults with ureteropelvic junction obstruction
- PMID: 22967009
- PMCID: PMC3593686
- DOI: 10.1089/end.2012.0017
Trends in the treatment of adults with ureteropelvic junction obstruction
Abstract
Background and purpose: Minimally invasive pyeloplasty is an effective treatment for patients with ureteropelvic junction obstruction that offers quicker convalescence than open pyeloplasty. Technical challenges, however, may have limited its dissemination. We examined population trends and determinants of surgical options for ureteropelvic junction obstruction.
Patients and methods: Using the State Inpatient and Ambulatory Surgery Databases for Florida, we identified adults who underwent ureteropelvic junction obstruction repair between 2001 and 2009. After determining the surgical approach (minimally invasive pyeloplasty, open pyeloplasty, or endopyelotomy), we estimated annual utilization rates and the effects of patient, surgeon, and hospital predictors on surgery type, using multilevel multinomial logistic regression.
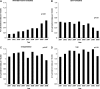
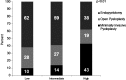
Results: Rates of minimally invasive pyeloplasty increased 360% (P for monotonic trend < 0.01), while rates of open pyeloplasty decreased 56% (P<0.01). Rates of endopyelotomy were substantially higher and remained relatively stable (P=0.27). Compared with open pyeloplasty, minimally invasive pyeloplasty was used more commonly among patients with private insurance (odds ratio [OR] 1.6; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.2-2.3), those treated at teaching hospitals (OR 1.6; CI 1.0-2.6), and those treated by high-volume surgeons (OR 2.9; CI 2.0-4.2). Its use was less frequent among patients with multiple comorbidities (OR 0.53; CI 0.37-0.76). Similar associations were observed when comparing receipt of minimally invasive pyeloplasty with endopyelotomy; however, patients who underwent endopyelotomy were older.
Conclusions: The use of minimally invasive pyeloplasty has dramatically increased, largely replacing open pyeloplasty, while the use of endopyelotomy, albeit significantly more common than the other approaches, has remained stable. The surgical approach is influenced by several patient, surgeon, and hospital factors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Minimally Invasive Techniques for the Management of Adult UPJ Obstruction.Curr Urol Rep. 2016 May;17(5):39. doi: 10.1007/s11934-016-0593-3. Curr Urol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26968419 Review.
-
Variation in the Use of Open Pyeloplasty, Minimally Invasive Pyeloplasty, and Endopyelotomy for the Treatment of Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction in Adults.J Endourol. 2017 Feb;31(2):210-215. doi: 10.1089/end.2016.0688. Epub 2017 Jan 5. J Endourol. 2017. PMID: 27936909 Free PMC article.
-
Cost Analysis of Treatments for Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction.J Endourol. 2017 Feb;31(2):204-209. doi: 10.1089/end.2016.0722. Epub 2017 Jan 5. J Endourol. 2017. PMID: 27927021 Free PMC article.
-
Equivocal ureteropelvic junction obstruction on diuretic renogram--should minimally invasive pyeloplasty be offered to symptomatic patients?J Urol. 2015 Apr;193(4):1278-82. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.10.100. Epub 2014 Oct 30. J Urol. 2015. PMID: 25444983
-
Minimally invasive treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction: a critical analysis of results.Eur Urol. 2007 Oct;52(4):983-9. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.06.047. Epub 2007 Jul 6. Eur Urol. 2007. PMID: 17629395 Review.
Cited by
-
Hospital-level Variation in the Quality of Benign Inpatient Urologic Surgery.Urology. 2016 Jan;87:82-7. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2015.07.067. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Urology. 2016. PMID: 26519000 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally Invasive Techniques for the Management of Adult UPJ Obstruction.Curr Urol Rep. 2016 May;17(5):39. doi: 10.1007/s11934-016-0593-3. Curr Urol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26968419 Review.
-
Variation in the Use of Open Pyeloplasty, Minimally Invasive Pyeloplasty, and Endopyelotomy for the Treatment of Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction in Adults.J Endourol. 2017 Feb;31(2):210-215. doi: 10.1089/end.2016.0688. Epub 2017 Jan 5. J Endourol. 2017. PMID: 27936909 Free PMC article.
-
Robot-assisted pyeloplasty: The way forward.J Minim Access Surg. 2021 Apr-Jun;17(2):274-275. doi: 10.4103/jmas.JMAS_59_20. J Minim Access Surg. 2021. PMID: 32964878 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cost Analysis of Treatments for Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction.J Endourol. 2017 Feb;31(2):204-209. doi: 10.1089/end.2016.0722. Epub 2017 Jan 5. J Endourol. 2017. PMID: 27927021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonnard A. Fouquet V. Carricaburu E, et al. Retroperitoneal laparoscopic versus open pyeloplasty in children. J Urol. 2005;173:1710–1713. - PubMed
-
- Klingler HC. Remzi M. Janetschek G, et al. Comparison of open versus laparoscopic pyeloplasty techniques in treatment of uretero-pelvic junction obstruction. Eur Urol. 2003;44:340–345. - PubMed
-
- Siqueira TM., Jr Nadu A. Kuo RL, et al. Laparoscopic treatment for ureteropelvic junction obstruction. Urology. 2002;60:973–978. - PubMed
-
- Yanke BV. Lallas CD. Pagnani C, et al. The minimally invasive treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction: A review of our experience during the last decade. J Urol. 2008;180:1397–1402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

