Autoimmunity to isomerized histone H2B in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 22967069
- PMCID: PMC3543506
- DOI: 10.3109/08916934.2012.710859
Autoimmunity to isomerized histone H2B in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
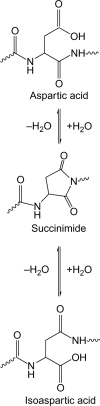
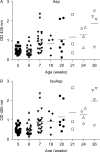
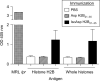
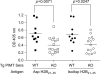
Histone H2B is a common target of autoantibodies in both spontaneous and drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Recent studies demonstrate that Asp(25) of histone H2B (H2B) spontaneously converts to an isoaspartic acid (isoAsp) in vivo. Our laboratory has demonstrated that the posttranslational modification of an aspartic acid to an isoaspartic acid within self-peptides renders otherwise ignored peptides immunogenic. Analysis of serum from lupus-prone mice and histone antibody positive SLE patients revealed antibodies specific to the Asp and isoAsp H2B(21-35) peptide, and that the expression of these antibodies is dependent on TLR9. IsoAsp H2B(21-35) is immunogenic in non-autoimmune prone mice and mice lacking the ability to repair isoAsp have significantly reduced levels of antibodies to H2B. Asp H2B(21-35) incubated at physiological temperatures and pH acquires the isoAsp modification, demonstrating that H2B(21-35) is prone to spontaneous isoAsp formation in vivo. Autoimmunity to isoAsp H2B suggests that this form of the autoantigen may be critical in the induction of anti-histone autoantibodies in human SLE and in murine models of disease.
Figures



References
-
- Mamula MJ, Gee RJ, Elliot JI, et al. Isoaspartyl post-translational modification triggers autoimmune responses to self-proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:22321–22327. - PubMed
-
- Clarke S. Protein carboxyl methyltransferases: Two distinct classes of enzymes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1985;54:479–506. - PubMed
-
- Young AL, Carter WG, Doyle HA, Mamula MJ, Aswad DW. Structural integrity of histone H2B in vivo requires the activity of protein L-isoaspartate O-methyltransferase, a putative protein repair enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:37161–37165. - PubMed
-
- Young GW, Hoofring SA, Mamula MJ, et al. Protein L-isoaspartyl methyltransferase catalyzes in vivo racemization of Aspartate-25 in mammalian histone H2B. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:26094–26098. - PubMed
-
- Aswad DW, Paranandi MV, Schurter BT. Isoaspartate in peptides and proteins: formation, significance, and analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000;21:1129–1136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
