A novel gene, ardD, determines antirestriction activity of the non-conjugative transposon Tn5053 and is located antisense within the tniA gene
- PMID: 22967207
- PMCID: PMC3533173
- DOI: 10.1111/1574-6968.12005
A novel gene, ardD, determines antirestriction activity of the non-conjugative transposon Tn5053 and is located antisense within the tniA gene
Abstract
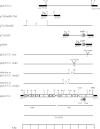
The mercury-resistance transposon Tn5053 inhibits restriction activity of the type I restriction-modification endonuclease EcoKI in Escherichia coli K12 cells. This is the first report of antirestriction activity of a non-conjugative transposon. The gene (ardD) coding for the antirestriction protein has been cloned. The ardD gene is located within the tniA gene, coding for transposase, on the complementary strand. The direction of transcription is opposite to transcription of the tniA gene.
© 2012 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

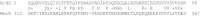
Similar articles
-
[Antirestriction activity of the mercury resistance nonconjugative transposon Tn5053 is controlled by the protease ClpXP].Genetika. 2014 Sep;50(9):1033-9. Genetika. 2014. PMID: 25735133 Russian.
-
[Proteolytic control of the antirestriction activity of Tn2l, Tn5053, Tn5045 Tn501 TN402 non-conjugative transposons].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2015 Mar-Apr;49(2):334-41. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2015. PMID: 26065261 Russian.
-
[Comparative analysis of antirestriction activity of R64 ArdA and ArdB proteins].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2012 Mar-Apr;46(2):269-75. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2012. PMID: 22670523 Russian.
-
[Antirestriction activity of the IncI1 transmissive plasmid R64 ArdA protein].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2004 Sep-Oct;38(5):901-6. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2004. PMID: 15554191 Russian.
-
[Antirestriction proteins ardA and Ocr as effective inhibitors of the type I restriction-modification enzymes].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2009 Mar-Apr;43(2):264-73. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2009. PMID: 19425495 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Three Novel Antisense Overlapping Genes in E. coli O157:H7 EDL933.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0235122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02351-22. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36533921 Free PMC article.
-
Hundreds of Out-of-Frame Remodeled Gene Families in the Escherichia coli Pangenome.Mol Biol Evol. 2022 Jan 7;39(1):msab329. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab329. Mol Biol Evol. 2022. PMID: 34792602 Free PMC article.
-
RecA-dependent or independent recombination of plasmid DNA generates a conflict with the host EcoKI immunity by launching restriction alleviation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 May 22;52(9):5195-5208. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae243. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38567730 Free PMC article.
-
The novel EHEC gene asa overlaps the TEGT transporter gene in antisense and is regulated by NaCl and growth phase.Sci Rep. 2018 Dec 14;8(1):17875. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35756-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30552341 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Sequence Analysis of the Multidrug-Resistance Region of Avian Salmonella enterica serovar Indiana Strain MHYL.Microorganisms. 2019 Aug 9;7(8):248. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7080248. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31404981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belogurov AA, Delver EP, Agafonova OV, Belogurova NG, Lee LY, Ado CI. Antirestriction protein Ard (Type C) encoded by IncW plasmid pSa has a high similarity to the “protein transport” domain of TraC1 primase of promiscuous plasmid RP4. J Mol Biol. 2000;296:969–977. - PubMed
-
- Fluit AC, Schmitz FJ. Class1 integrons, gene cassettes, mobility, and epidemiology. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1999;18:761–770. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

