In silico-aided design of a glycan ligand of sialoadhesin for in vivo targeting of macrophages
- PMID: 22967315
- PMCID: PMC3462166
- DOI: 10.1021/ja307501e
In silico-aided design of a glycan ligand of sialoadhesin for in vivo targeting of macrophages
Abstract
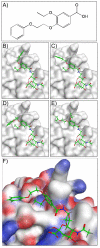
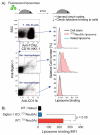
Cell-specific delivery of therapeutic agents using ligand targeting is gaining interest because of its potential for increased efficacy and reduced side effects. The challenge is to develop a suitable ligand for a cell-surface receptor that is selectively expressed on the desired cell. Sialoadhesin (Sn, Siglec-1, CD169), a sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec) expressed on subsets of resident and inflammatory macrophages, is an attractive target for the development of a ligand-targeted delivery system. Here we report the development of a high-affinity and selective ligand for Sn that is an analogue of the natural ligand and is capable of targeting liposomal nanoparticles to Sn-expressing cells in vivo. An efficient in silico screen of a library of ∼8400 carboxylic acids was the key to identifying novel 9-N-acyl-substituted N-acetylneuramic acid (Neu5Ac) substituents as potential lead compounds. A small panel of targets were selected from the screen and synthesized to evaluate their affinities and selectivities. The most potent of these Sn ligands, 9-N-(4H-thieno[3,2-c]chromene-2-carbamoyl)-Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-4GlcNAc ((TCC)Neu5Ac), was conjugated to lipids for display on a liposomal nanoparticle for evaluation of targeted delivery to cells. The (TCC)Neu5Ac liposomes were found to target liposomes selectively to cells expressing either murine or human Sn in vitro, and when administered to mice, they exhibited in vivo targeting to Sn-positive macrophages.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antigen delivery to macrophages using liposomal nanoparticles targeting sialoadhesin/CD169.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039039. Epub 2012 Jun 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22723922 Free PMC article.
-
A Sulfonamide Sialoside Analogue for Targeting Siglec-8 and -F on Immune Cells.J Am Chem Soc. 2019 Sep 11;141(36):14032-14037. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b05769. Epub 2019 Aug 30. J Am Chem Soc. 2019. PMID: 31460762 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted delivery of lipid antigen to macrophages via the CD169/sialoadhesin endocytic pathway induces robust invariant natural killer T cell activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 May 7;110(19):7826-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219888110. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23610394 Free PMC article.
-
Sialoadhesin - a macrophage-restricted marker of immunoregulation and inflammation.Immunology. 2013 Mar;138(3):198-207. doi: 10.1111/imm.12042. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23181380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sialic acid binding receptors (siglecs) expressed by macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Nov;66(5):705-11. doi: 10.1002/jlb.66.5.705. J Leukoc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10577497 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Siglecs on autoimmune diseases.Mol Aspects Med. 2023 Apr;90:101140. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2022.101140. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Mol Aspects Med. 2023. PMID: 36055802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the use of abiotic sialic acids to attenuate cell inflammation.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 23;8(1):17320. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35477-2. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30470771 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Macrophages M1/M2 Polarization Using Carbohydrate-Functionalized Polymeric Nanoparticles.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Dec 28;13(1):88. doi: 10.3390/polym13010088. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33379389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycotherapy: new advances inspire a reemergence of glycans in medicine.Chem Biol. 2014 Jan 16;21(1):16-37. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 24269151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Siglecs using Antibody- and Glycan-Based Approaches.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Oct;36(10):645-660. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2015.06.008. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26435210 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torchilin VP. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:145. - PubMed
-
- Trapani G, Denora N, Trapani A, Laquintana V. J Drug Target. 2012;20:1. - PubMed
-
- Lepenies B, Yin JA, Seeberger PH. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010;14:404. - PubMed
-
- Jain K, Kesharwani P, Gupta U, Jain NK. Biomaterials. 2012;33:4166. - PubMed
-
- Xie R, Hong SL, Feng LS, Rong J, Chen X. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:9914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

