Insulin fails to enhance mTOR phosphorylation, mitochondrial protein synthesis, and ATP production in human skeletal muscle without amino acid replacement
- PMID: 22967500
- PMCID: PMC3492854
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00067.2012
Insulin fails to enhance mTOR phosphorylation, mitochondrial protein synthesis, and ATP production in human skeletal muscle without amino acid replacement
Abstract
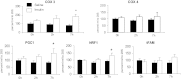
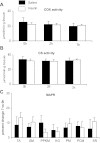
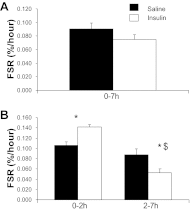
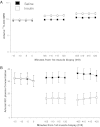
Systemic insulin administration causes hypoaminoacidemia by inhibiting protein degradation, which may in turn inhibit muscle protein synthesis (PS). Insulin enhances muscle mitochondrial PS and ATP production when hypoaminoacidemia is prevented by exogenous amino acid (AA) replacement. We determined whether insulin would stimulate mitochondrial PS and ATP production in the absence of AA replacement. Using l-[1,2-¹³C]leucine as a tracer, we measured the fractional synthetic rate of mitochondrial as well as sarcoplasmic and mixed muscle proteins in 18 participants during sustained (7-h) insulin or saline infusion (n = 9 each). We also measured muscle ATP production, mitochondrial enzyme activities, mRNA levels of mitochondrial genes, and phosphorylation of signaling proteins regulating protein synthesis. The concentration of circulating essential AA decreased during insulin infusion. Mitochondrial, sarcoplasmic, and mixed muscle PS rates were also lower during insulin (2-7 h) than during saline infusions despite increased mRNA levels of selected mitochondrial genes. Under these conditions, insulin did not alter mitochondrial enzyme activities and ATP production. These effects were associated with enhanced phosphorylation of Akt but not of protein synthesis activators mTOR, p70(S6K), and 4EBP1. In conclusion, sustained physiological hyperinsulinemia without AA replacement did not stimulate PS of mixed muscle or protein subfractions and did not alter muscle mitochondrial ATP production in healthy humans. These results support that insulin and AA act in conjunction to stimulate muscle mitochondrial function and mitochondrial protein synthesis.
Figures


References
-
- Asmann YW, Stump CS, Short KR, Coenen-Schimke JM, Guo Z, Bigelow M, Nair KS. Skeletal muscle mitochondrial functions, mitochondrial DNA copy numbers, and gene transcript profiles in type 2 diabetic and nondiabetic subjects at equal levels of low or high insulin and euglycemia. Diabetes 55: 3309–3319, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Balagopal P, Ford GC, Ebenstein DB, Nadeau DA, Nair KS. Mass spectrometric methods for determination of [13C]leucine enrichment in human muscle protein. Anal Biochem 239: 77–85, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Chow LS, Albright RC, Bigelow ML, Toffolo G, Cobelli C, Nair KS. Mechanism of insulin's anabolic effect on muscle: measurements of muscle protein synthesis and breakdown using aminoacyl-tRNA and other surrogate measures. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 291: E729–E736, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Cunningham JT, Rodgers JT, Arlow DH, Vazquez F, Mootha VK, Puigserver P. mTOR controls mitochondrial oxidative function through a YY1-PGC-1[agr] transcriptional complex. Nature 450: 736–740, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

