Collaborative interplay between FGF-2 and VEGF-C promotes lymphangiogenesis and metastasis
- PMID: 22967508
- PMCID: PMC3465417
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1208324109
Collaborative interplay between FGF-2 and VEGF-C promotes lymphangiogenesis and metastasis
Abstract
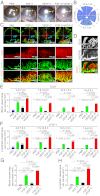
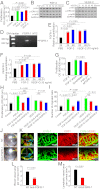
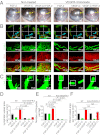
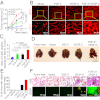
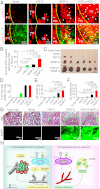
Interplay between various lymphangiogenic factors in promoting lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis remains poorly understood. Here we show that FGF-2 and VEGF-C, two lymphangiogenic factors, collaboratively promote angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in the tumor microenvironment, leading to widespread pulmonary and lymph-node metastases. Coimplantation of dual factors in the mouse cornea resulted in additive angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. At the molecular level, we showed that FGFR-1 expressed in lymphatic endothelial cells is a crucial receptor that mediates the FGF-2-induced lymphangiogenesis. Intriguingly, the VEGFR-3-mediated signaling was required for the lymphatic tip cell formation in both FGF-2- and VEGF-C-induced lymphangiogenesis. Consequently, a VEGFR-3-specific neutralizing antibody markedly inhibited FGF-2-induced lymphangiogenesis. Thus, the VEGFR-3-induced lymphatic endothelial cell tip cell formation is a prerequisite for FGF-2-stimulated lymphangiogenesis. In the tumor microenvironment, the reciprocal interplay between FGF-2 and VEGF-C collaboratively stimulated tumor growth, angiogenesis, intratumoral lymphangiogenesis, and metastasis. Thus, intervention and targeting of the FGF-2- and VEGF-C-induced angiogenic and lymphangiogenic synergism could be potentially important approaches for cancer therapy and prevention of metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fidler IJ, Ellis LM. The implications of angiogenesis for the biology and therapy of cancer metastasis. Cell. 1994;79:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Rouhi P, et al. Hypoxia-induced metastasis model in embryonic zebrafish. Nat Protoc. 2010;5:1911–1918. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y. Opinion: Emerging mechanisms of tumour lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:735–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

