Rhythmic ring-ring stacking drives the circadian oscillator clockwise
- PMID: 22967510
- PMCID: PMC3479483
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1211508109
Rhythmic ring-ring stacking drives the circadian oscillator clockwise
Abstract
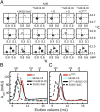
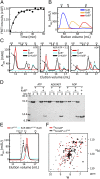
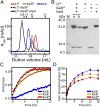
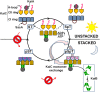
The oscillator of the circadian clock of cyanobacteria is composed of three proteins, KaiA, KaiB, and KaiC, which together generate a self-sustained ∼24-h rhythm of phosphorylation of KaiC. The mechanism propelling this oscillator has remained elusive, however. We show that stacking interactions between the CI and CII rings of KaiC drive the transition from the phosphorylation-specific KaiC-KaiA interaction to the dephosphorylation-specific KaiC-KaiB interaction. We have identified the KaiB-binding site, which is on the CI domain. This site is hidden when CI domains are associated as a hexameric ring. However, stacking of the CI and CII rings exposes the KaiB-binding site. Because the clock output protein SasA also binds to CI and competes with KaiB for binding, ring stacking likely regulates clock output. We demonstrate that ADP can expose the KaiB-binding site in the absence of ring stacking, providing an explanation for how it can reset the clock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Bacterial physiology: uncovering the circadian clockwork.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Nov;10(11):730. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2896. Epub 2012 Oct 8. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23042565 No abstract available.
-
Orderly wheels of the cyanobacterial clock.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 16;109(42):16760-1. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1214901109. Epub 2012 Oct 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23045681 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hogenesch JB, Ueda HR. Understanding systems-level properties: Timely stories from the study of clocks. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:407–416. - PubMed
-
- Ishiura M, et al. Expression of a gene cluster kaiABC as a circadian feedback process in cyanobacteria. Science. 1998;281:1519–1523. - PubMed
-
- Tomita J, Nakajima M, Kondo T, Iwasaki H. No transcription-translation feedback in circadian rhythm of KaiC phosphorylation. Science. 2005;307:251–254. - PubMed
-
- Nakajima M, et al. Reconstitution of circadian oscillation of cyanobacterial KaiC phosphorylation in vitro. Science. 2005;308:414–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

