Mechanisms involved in PGE2-induced transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in MH1C1 hepatocarcinoma cells
- PMID: 22967907
- PMCID: PMC3542006
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-31-72
Mechanisms involved in PGE2-induced transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in MH1C1 hepatocarcinoma cells
Abstract
Background: It is important to understand the mechanisms by which the cells integrate signals from different receptors. Several lines of evidence implicate epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor (EGFR) in the pathophysiology of hepatocarcinomas. Data also suggest a role of prostaglandins in some of these tumours, through their receptors of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. In this study we have investigated mechanisms of interaction between signalling from prostaglandin receptors and EGFR in hepatocarcinoma cells.
Methods: The rat hepatocarcinoma cell line MH1C1 and normal rat hepatocytes in primary culture were stimulated with EGF or prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and in some experiments also PGF2α. DNA synthesis was determined by incorporation of radiolabelled thymidine into DNA, phosphorylation of proteins in signalling pathways was assessed by Western blotting, mRNA expression of prostaglandin receptors was determined using qRT-PCR, accumulation of inositol phosphates was measured by incorporation of radiolabelled inositol, and cAMP was determined by radioimmunoassay.
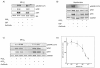
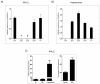
Results: In the MH1C1 hepatocarcinoma cells, stimulation with PGE2 or PGF2α caused phosphorylation of the EGFR, Akt, and ERK, which could be blocked by the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib. This did not occur in primary hepatocytes. qRT-PCR revealed expression of EP1, EP4, and FP receptor mRNA in MH1C1 cells. PGE2 stimulated accumulation of inositol phosphates but not cAMP in these cells, suggesting signalling via PLCβ. While pretreatment with EP1 and EP4 receptor antagonists did not inhibit the effect of PGE2, pretreatment with an FP receptor antagonist blocked the phosphorylation of EGFR, Akt and ERK. Further studies suggested that the PGE2-induced signal was mediated via Ca2+ release and not PKC activation, and that it proceeded through Src and shedding of membrane-bound EGFR ligand precursors by proteinases of the ADAM family.
Conclusion: The results indicate that in MH1C1 cells, unlike normal hepatocytes, PGE2 activates the MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways by transactivation of the EGFR, thus diversifying the GPCR-mediated signal. The data also suggest that the underlying mechanisms in these cells involve FP receptors, PLCβ, Ca2+, Src, and proteinase-mediated release of membrane-associated EGFR ligand(s).
Figures




References
-
- Prenzel N, Zwick E, Daub H, Leserer M, Abraham R, Wallasch C, Ullrich A. EGF receptor transactivation by G-protein-coupled receptors requires metalloproteinase cleavage of proHB-EGF. Nature. 1999;402(6764):884–888. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

