Double-dissociation of D1 and opioid receptor antagonism effects on the acquisition of sucrose-conditioned flavor preferences in BALB/c and SWR mice
- PMID: 22967990
- PMCID: PMC3444661
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2012.07.018
Double-dissociation of D1 and opioid receptor antagonism effects on the acquisition of sucrose-conditioned flavor preferences in BALB/c and SWR mice
Abstract
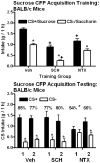
Sugar appetite is influenced by unlearned attractions to sweet taste and learned responses to sugars' taste and post-ingestive actions. In rats, sugar-conditioned flavor preferences (CFP) are attenuated by dopamine D1 (SCH23390: SCH), but not by opioid (naltrexone: NTX), receptor antagonism. Sucrose-CFP occurs in BALB/c and SWR inbred mice that differ in their suppressive effects of SCH and NTX on sucrose intake. The present study examined whether SCH and NTX altered expression of previously learned sucrose-CFP and acquisition (learning) of sucrose-CFP in these strains. In Experiment 1, food-restricted mice were trained (10 one-bottle sessions) to drink a more-preferred flavored (e.g., cherry) 16% sucrose solution (CS+/Sucrose) on odd-numbered days, and a less-preferred flavored (e.g., grape) 0.05% saccharin solution (CS-/Saccharin) on even-numbered days. Two-bottle tests with the flavors mixed in 0.2% saccharin occurred 30 min following vehicle (Veh), SCH (50-800 nmol/kg) or NTX (1-5mg/kg) assessing preference expression. CS+ preference expression in BALB/c and SWR mice following Veh were significantly reduced by SCH and NTX. In Experiment 2, separate groups of BALB/c and SWR mice received Veh, SCH (50 nmol/kg) or NTX (1mg/kg) injections 30 min prior to daily one-bottle training sessions with the CS+/Sucrose and CS-/Saccharin solutions assessing preference acquisition. Subsequent two-bottle tests with the CS+ vs. CS- solutions were conducted without injections. CS+/Sucrose training intakes were reduced by SCH in both strains and by NTX in BALB/c mice. In the initial two-bottle test, sucrose-CFP acquisition was significantly reduced in BALB NTX (54%), but not in BALB SCH (77%) groups relative to the BALB Veh group (85%). In contrast, sucrose-CFP acquisition was significantly reduced in SWR SCH (61%), but not in SWR NTX (83%) groups relative to the SWR Veh group (86%). DA D1 and opioid receptor signaling modulate acquisition and/or expression of sucrose-CFP in mice with significant strain differences observed.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Azzara AV, Bodnar RJ, Delamater AR, Sclafani A. Naltrexone fails to block the acquisition or expression of a flavor preference conditioned by intragastric carbohydrate infusions. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000;67:545–557. - PubMed
-
- Azzara AV, Bodnar RJ, Delamater AR, Sclafani A. D-1 but not D-2 dopamine receptor antagonism blocks the acquisition of a flavor preference conditioned by intragastric carbohydrate infusions. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2001;68:709–720. - PubMed
-
- Baker RM, Li Y, Lee M, Sclafani A, Bodnar RJ. Naltrexone does not prevent acquisition or expression of flavor preferences conditioned by fructose in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2004;78:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Baker RM, Shah MJ, Sclafani A, Bodnar RJ. Dopamine D1 and D2 antagonists reduce the acquisition and expression of flavor-preferences conditioned by fructose in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2003;75:55–65. - PubMed
-
- Belknap JK, Crabbe JC, Riggan J, O’Toole LA. Voluntary consumption of morphine in 15 inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacol. 1993;112:352–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

