Next-generation sequencing (NGS) as a diagnostic tool for retinal degeneration reveals a much higher detection rate in early-onset disease
- PMID: 22968130
- PMCID: PMC3573204
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.172
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) as a diagnostic tool for retinal degeneration reveals a much higher detection rate in early-onset disease
Erratum in
- Eur J Hum Genet. 2013 Sep;21(9):1031
Abstract
Inherited retinal degeneration (IRD) is a common cause of visual impairment (prevalence ∼1/3500). There is considerable phenotype and genotype heterogeneity, making a specific diagnosis very difficult without molecular testing. We investigated targeted capture combined with next-generation sequencing using Nimblegen 12plex arrays and the Roche 454 sequencing platform to explore its potential for clinical diagnostics in two common types of IRD, retinitis pigmentosa and cone-rod dystrophy. 50 patients (36 unknowns and 14 positive controls) were screened, and pathogenic mutations were identified in 25% of patients in the unknown, with 53% in the early-onset cases. All patients with new mutations detected had an age of onset <21 years and 44% had a family history. Thirty-one percent of mutations detected were novel. A de novo mutation in rhodopsin was identified in one early-onset case without a family history. Bioinformatic pipelines were developed to identify likely pathogenic mutations and stringent criteria were used for assignment of pathogenicity. Analysis of sequencing metrics revealed significant variability in capture efficiency and depth of coverage. We conclude that targeted capture and next-generation sequencing are likely to be very useful in a diagnostic setting, but patients with earlier onset of disease are more likely to benefit from using this strategy. The mutation-detection rate suggests that many patients are likely to have mutations in novel genes.
Figures
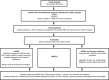

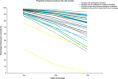
References
-
- Jaakson K, Zernant J, Külm M, et al. Genotyping microarray (gene chip) for the ABCR (ABCA4) gene. Hum Mutat. 2003;22:395–403. - PubMed
-
- Klevering BJ, Yzer S, Rohrschneider K, et al. Microarray-based mutation analysis of the ABCA4 (ABCR) gene in autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophy and retinitis pigmentosa. Eur J Hum Genet. 2004;12:1024–1032. - PubMed
-
- World Medical Association World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. J Postgrad Med. 2002;48:206–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

