MiR-351 transiently increases during muscle regeneration and promotes progenitor cell proliferation and survival upon differentiation
- PMID: 22968638
- PMCID: PMC3524771
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00052.2012
MiR-351 transiently increases during muscle regeneration and promotes progenitor cell proliferation and survival upon differentiation
Abstract
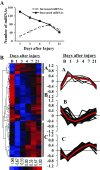
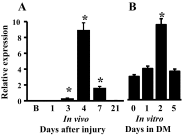
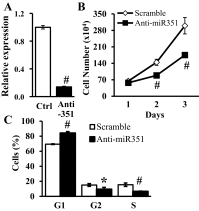
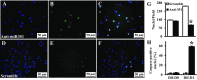
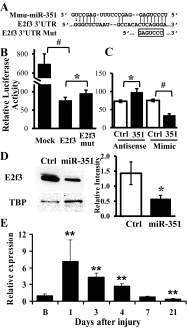
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate many biological processes including muscle development. However, little is known regarding miRNA regulation of muscle regeneration. Murine tibialis anterior muscle was evaluated after cardiotoxin-induced injury and used for global miRNA expression analysis. From day 1 through day 21 following injury, 298 miRNAs were significantly changed at least at one time point, including 86 miRNAs that were altered >10-fold compared with uninjured skeletal muscle. Temporal miRNA expression patterns included inflammation-related miRNAs (miR-223 and -147) that increased immediately after injury; this pattern contrasted to that of mature muscle-specific miRNAs (miR-1, -133a, and -499) that abruptly decreased following injury followed by upregulation in later regenerative events. Another cluster of miRNAs were transiently increased in the early days of muscle regeneration including miR-351, a miRNA that was also transiently expressed during myogenic progenitor cell (MPC) differentiation in vitro. Based on computational predictions, further studies demonstrated that E2f3 was a target of miR-351 in myoblasts. Moreover, knockdown of miR-351 expression inhibited MPC proliferation and promoted apoptosis during MPC differentiation, whereas miR-351 overexpression protected MPC from apoptosis during differentiation. Collectively, these observations suggest that miR-351 is involved in both the maintenance of MPC proliferation and the transition into differentiated myotubes. Thus, a novel, time-dependent sequence of molecular events during muscle regeneration has been identified; miR-351 inhibits E2f3 expression, a key regulator of cell cycle progression and proliferation, and promotes MPC proliferation and protects early differentiating MPC from apoptosis, important events in the hostile tissue environment after acute muscle injury.
Figures

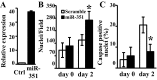

References
-
- Anderson JE, Murray L. Barr Award Lecture. Studies of the dynamics of skeletal muscle regeneration: the mouse came back! Biochem Cell Biol 76: 13–26, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Antonini D, Russo MT, De Rosa L, Gorrese M, Del Vecchio L, Missero C. Transcriptional repression of miR-34 family contributes to p63-mediated cell cycle progression in epidermal cells. J Invest Dermatol 130: 1249–1257, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Cam H, Dynlacht BD. Emerging roles for E2F: beyond the G1/S transition and DNA replication. Cancer Cell 3: 311–316, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

