Perilymph pharmacokinetics of markers and dexamethasone applied and sampled at the lateral semi-circular canal
- PMID: 22968908
- PMCID: PMC3505589
- DOI: 10.1007/s10162-012-0347-y
Perilymph pharmacokinetics of markers and dexamethasone applied and sampled at the lateral semi-circular canal
Abstract
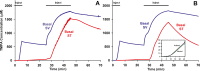
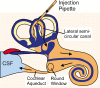
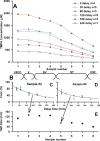
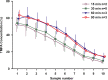
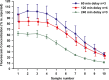
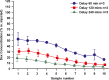
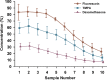
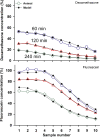
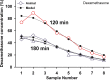
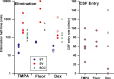
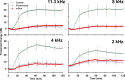
Perilymph pharmacokinetics was investigated by a novel approach, in which solutions containing drug or marker were injected from a pipette sealed into the perilymphatic space of the lateral semi-circular canal (LSCC). The cochlear aqueduct provides the outlet for fluid flow so this procedure allows almost the entire perilymph to be exchanged. After wait times of up to 4 h the injection pipette was removed and multiple, sequential samples of perilymph were collected from the LSCC. Fluid efflux at this site results from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) entry into the basal turn of scala tympani (ST) so the samples allow drug levels from different locations in the ear to be defined. This method allows the rate of elimination of substances from the inner ear to be determined more reliably than with other delivery methods in which drug may only be applied to part of the ear. Results were compared for the markers trimethylphenylammonium (TMPA) and fluorescein and for the drug dexamethasone (Dex). For each substance, the concentration in fluid samples showed a progressive decrease as the delay time between injection and sampling was increased. This is consistent with the elimination of substance from the ear with time. The decline with time was slowest for fluorescein, was fastest for Dex, with TMPA at an intermediate rate. Simulations of the experiments showed that elimination occurred more rapidly from scala tympani (ST) than from scala vestibuli (SV). Calculated elimination half-times from ST averaged 54.1, 24.5 and 22.5 min for fluorescein, TMPA and Dex respectively and from SV 1730, 229 and 111 min respectively. The elimination of Dex from ST occurred considerably faster than previously appreciated. These pharmacokinetic parameters provide an important foundation for understanding of drug treatments of the inner ear.
Figures
References
-
- Borden RC, Saunders JE, Berryhill WE, et al. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel sustains the delivery of dexamethasone across the round window membrane. Audiol Neurootol. 2011;16:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Chandrasekhar SS, Rubinstein RY, Kwartler JA, Gatz M, Connelly PE, Huang E, Baredes S. Dexamethasone pharmacokinetics in the inner ear: comparison of route of administration and use of facilitating agents. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000;122:521–528. doi: 10.1016/S0194-5998(00)70094-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

