Fluid circulation determined in the isolated bovine lens
- PMID: 22969071
- PMCID: PMC3471605
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.12-10295
Fluid circulation determined in the isolated bovine lens
Abstract
Purpose: In 1997, a theoretical model was developed that predicted the existence of an internal, Na(+)-driven fluid circulation from the poles to the equator of the lens. In the present work, we demonstrate with a novel system that fluid movement can be measured across the polar and equatorial surface areas of isolated cow lenses. We have also determined the effects of ouabain and reduced bath [Na(+)].
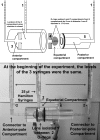
Methods: Lenses were isolated in a chamber with three compartments separated by two thin O-rings. Each compartment, anterior (A), equatorial (E), and posterior (P), was connected to a vertical capillary graduated in 0.25 μL. Capillary levels were read every 15 minutes. The protocols consisted of 2 hours in either open circuit or short circuit. The effects of ouabain and low-Na(+) solutions were determined under open circuit.
Results: In 21 experiments, the E capillary increased at a mean rate of 0.060 μL/min while the A and P levels decreased at rates of 0.044 and 0.037 μL/min, respectively, closely accounting for the increase in E. The first-hour flows under short circuit were approximately 40% larger than those in open-circuit conditions. The first-hour flows were always larger than those during the second hour. Preincubation of lenses with either ouabain or low-[Na(+)] solutions resulted in reduced rates of fluid transport. When KCl was used to replace NaCl, a transitory stimulation of fluid transport occurred.
Conclusions: These experiments support that a fluid circulation consistent with the 1997 model is physiologically active.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures



References
-
- Mathias RT, Rae JL, Baldo GJ. Physiological properties of the normal lens. Physiol Rev. 1997;77:21–50 - PubMed
-
- Mathias RT, Kistler J, Donaldson P. The lens circulation. J Membr Biol. 2007;216:1–16 - PubMed
-
- Robinson KR, Patterson JW. Localization of steady currents in the lens. Curr Eye Res. 1982;2:843–847 - PubMed
-
- Patterson JW. Characterization of the equatorial current of the lens. Ophthalmic Res. 1988;20:139–142 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

