Disruption of P450-mediated vitamin E hydroxylase activities alters vitamin E status in tocopherol supplemented mice and reveals extra-hepatic vitamin E metabolism
- PMID: 22969154
- PMCID: PMC3494260
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M030734
Disruption of P450-mediated vitamin E hydroxylase activities alters vitamin E status in tocopherol supplemented mice and reveals extra-hepatic vitamin E metabolism
Abstract
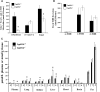
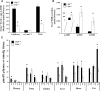
The widely conserved preferential accumulation of α-tocopherol (α-TOH) in tissues occurs, in part, from selective postabsorptive catabolism of non-α-TOH forms via the vitamin E-ω-oxidation pathway. We previously showed that global disruption of CYP4F14, the major but not the only mouse TOH-ω-hydroxylase, resulted in hyper-accumulation of γ-TOH in mice fed a soybean oil diet. In the current study, supplementation of Cyp4f14(-/-) mice with high levels of δ- and γ-TOH exacerbated tissue enrichment of these forms of vitamin E. However, at high dietary levels of TOH, mechanisms other than ω-hydroxylation dominate in resisting diet-induced accumulation of non-α-TOH. These include TOH metabolism via ω-1/ω-2 oxidation and fecal elimination of unmetabolized TOH. The ω-1 and ω-2 fecal metabolites of γ- and α-TOH were observed in human fecal material. Mice lacking all liver microsomal CYP activity due to disruption of cytochrome P450 reductase revealed the presence of extra-hepatic ω-, ω-1, and ω-2 TOH hydroxylase activities. TOH-ω-hydroxylase activity was exhibited by microsomes from mouse and human small intestine; murine activity was entirely due to CYP4F14. These findings shed new light on the role of TOH-ω-hydroxylase activity and other mechanisms in resisting diet-induced accumulation of tissue TOH and further characterize vitamin E metabolism in mice and humans.
Figures


References
-
- Bieri J. G., Evarts R. P. 1973. Tocopherols and fatty acids in American diets. The recommended allowance for vitamin E. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 62: 147–151 - PubMed
-
- Dial S., Eitenmiller R. R.1995. Tocopherols and tocotrienols in key foods in the U.S. diet. In Nutrition, Lipids, Health, and Disease. A. S. H. Ong, E. Niki, and L. Packer, editors. AOCS Press, Champaign, IL. 327–342.
-
- Ford E. S., Schleicher R. L., Mokdad A. H., Ajani U. A., Liu S. M. 2006. Distribution of serum concentrations of alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol in the US population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 84: 375–383 - PubMed
-
- Yoshida Y., Niki E., Noguchi N. 2003. Comparative study on the action of tocopherols and tocotrienols as antioxidant: chemical and physical effects. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 123: 63–75 - PubMed
-
- Saito Y., Yoshida Y., Akazawa T., Takahashi K., Niki E. 2003. Cell death caused by selenium deficiency and protective effect of antioxidants. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 39428–39434 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

