Macrolide therapy in chronic inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 22969171
- PMCID: PMC3432395
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/636157
Macrolide therapy in chronic inflammatory diseases
Abstract
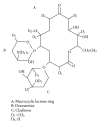
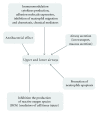
Macrolides are a group of antibiotics with a distinctive macrocyclic lactone ring combined with sugars (cladinose, desosamine). The action of macrolides is to block protein synthesis by binding to the subunit of 50S ribosome of bacteria. Prototype macrolide was erythromycin, which came into clinical practice in the 50s of the 20th century. Its antimicrobial spectrum covers the scope of the penicillins but is extended to the impact of atypical bacteria. In the 90 s more drugs of this group were synthesized-they have less severe side effects than erythromycin, extended spectrum of Gram-negative bacteria. Macrolides are effective in treating mycobacterial infections especially in patients infected with HIV. It is now known that in addition to antibacterial abilities, macrolides have immunomodulatory effects-they inhibit the production of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF, IL1, 6, and 8) affect transcription factors (NF-κB) as well as costimulaton (CD 80) and adhesion molecules (ICAM). This review article focused not only on the their antimicrobial abilities but also on efficacy in the treatment of several inflammatory disorders independent of the infectious agent. Their wider use as immunomodulators requires further study, which can lead to an extension of indications for their administration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical implications of the immunomodulatory effects of macrolides.Am J Med. 2004 Nov 8;117 Suppl 9A:5S-11S. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2004.07.023. Am J Med. 2004. PMID: 15586558 Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of macrolides--an underappreciated benefit in the treatment of community-acquired respiratory tract infections and chronic inflammatory pulmonary conditions?J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005 Jan;55(1):10-21. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkh519. Epub 2004 Dec 8. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15590715 Review.
-
The ketolides: a critical review.Drugs. 2002;62(12):1771-804. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262120-00006. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12149046 Review.
-
Past, present and future of macrolide therapy for chronic rhinosinusitis in Japan.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2016 Apr;43(2):131-6. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2015.08.014. Epub 2015 Oct 4. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2016. PMID: 26441370 Review.
-
Approaches to the synthesis of immunolides: selective immunomodulatory macrolides for cystic fibrosis.Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2005 Nov;8(6):741-7. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2005. PMID: 16312149 Review.
Cited by
-
The Chondroprotective Role of Erythromycin in a Murine Joint Destruction Model.Cartilage. 2016 Oct;7(4):373-87. doi: 10.1177/1947603516630787. Epub 2016 Feb 17. Cartilage. 2016. PMID: 27688845 Free PMC article.
-
Drug repositioning prediction for psoriasis using the adverse event reporting database.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 23;10:1159453. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1159453. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37035327 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria-A Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Aug 9;11(8):1079. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11081079. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and clinical manifestations of macrolide resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Korean children.Korean J Pediatr. 2017 May;60(5):151-157. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2017.60.5.151. Epub 2017 May 31. Korean J Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28592978 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of roxithromycin on mucosal damage, oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory markers in experimental model of colitis.Inflamm Res. 2018 Feb;67(2):147-155. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1103-x. Epub 2017 Oct 7. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 28988395
References
-
- Alekshun MN. New advances in antibiotic development and discovery. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 2005;14(2):117–134. - PubMed
-
- Wilson DN. The A-Z of bacterial translation inhibitors. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 2009;44:393–433. - PubMed
-
- Douthwaite S, Hansen LH, Mauvais P. Macrolide-ketolide inhibition of MLS-resistant ribosomes is improved by alternative drug interaction with domain II of 23S rRNA. Molecular Microbiology. 2000;36(1):183–192. - PubMed
-
- Katzung BGMacrolides. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. (9th edition) 2004;44
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical