Prevalence of functional dyspepsia and its subgroups in patients with eating disorders
- PMID: 22969202
- PMCID: PMC3436054
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i32.4379
Prevalence of functional dyspepsia and its subgroups in patients with eating disorders
Abstract
Aim: To study the prevalence of functional dyspepsia (FD) (Rome III criteria) across eating disorders (ED), obese patients, constitutional thinner and healthy volunteers.
Methods: Twenty patients affected by anorexia nervosa, 6 affected by bulimia nervosa, 10 affected by ED not otherwise specified according to diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edition, nine constitutional thinner subjects and, thirty-two obese patients were recruited from an outpatients clinic devoted to eating behavior disorders. Twenty-two healthy volunteers matched for age and gender were enrolled as healthy controls. All participants underwent a careful clinical examination. Demographic and anthropometric characteristics were obtained from a structured questionnaires. The presence of FD and, its subgroups, epigastric pain syndrome and postprandial distress syndrome (PDS) were diagnosed according to Rome III criteria. The intensity-frequency score of broader dyspeptic symptoms such as early satiety, epigastric fullness, epigastric pain, epigastric burning, epigastric pressure, belching, nausea and vomiting were studied by a standardized questionnaire (0-6). Analysis of variance and post-hoc Sheffè tests were used for comparisons.
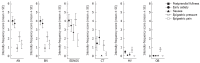
Results: 90% of patients affected by anorexia nervosa, 83.3% of patients affected by bulimia nervosa, 90% of patients affected by ED not otherwise specified, 55.6% of constitutionally thin subjects and 18.2% healthy volunteers met the Postprandial Distress Syndrome Criteria (χ(2), P < 0.001). Only one bulimic patient met the epigastric pain syndrome diagnosis. Postprandial fullness intensity-frequency score was significantly higher in anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa and ED not otherwise specified groups compared to the score calculated in the constitutional thinner group (4.15 ± 2.08 vs 1.44 ± 2.35, P = 0.003; 5.00 ± 2.45 vs 1.44 ± 2.35, P = 0.003; 4.10 ± 2.23 vs 1.44 ± 2.35, P = 0.002, respectively), the obese group (4.15 ± 2.08 vs 0.00 ± 0.00, P < 0.001; 5.00 ± 2.45 vs 0.00 ± 0.00, P < 0.001; 4.10 ± 2.23 vs 0.00 ± 0.00, P < 0.001, respectively) and healthy volunteers (4.15 ± 2.08 vs 0.36 ± 0.79, P < 0.001; 5.00 ± 2.45 vs 0.36 ± 0.79, P < 0.001; 4.10 ± 2.23 vs 0.36 ± 0.79, P < 0.001, respectively). Early satiety intensity-frequency score was prominent in anorectic patients compared to bulimic patients (3.85 ± 2.23 vs 1.17 ± 1.83, P = 0.015), obese patients (3.85 ± 2.23 vs 0.00 ± 0.00, P < 0.001) and healthy volunteers (3.85 ± 2.23 vs 0.05 ± 0.21, P < 0.001). Nausea and epigastric pressure were increased in bulimic and ED not otherwise specified patients. Specifically, nausea intensity-frequency-score was significantly higher in bulimia nervosa and ED not otherwise specified patients compared to anorectic patients (3.17 ± 2.56 vs 0.89 ± 1.66, P = 0.04; 2.70 ± 2.91 vs 0.89 ± 1.66, P = 0.05, respectively), constitutional thinner subjects (3.17 ± 2.56 vs 0.00 ± 0.00, P = 0.004; 2.70 ± 2.91 vs 0.00 ± 0.00, P = 0.005, respectively), obese patients (3.17 ± 2.56 vs 0.00 ± 0.00, P < 0.001; 3.17 ± 2.56 vs 0.00 ± 0.00, P < 0.001 respectively) and, healthy volunteers (3.17 ± 2.56 vs 0.17 ± 0.71, P = 0.002; 3.17 ± 2.56 vs 0.17 ± 0.71, P = 0.001, respectively). Epigastric pressure intensity-frequency score was significantly higher in bulimic and ED not otherwise specified patients compared to constitutional thin subjects (4.67 ± 2.42 vs 1.22 ± 1.72, P = 0.03; 4.20 ± 2.21 vs 1.22 ± 1.72, P = 0.03, respectively), obese patients (4.67 ± 2.42 vs 0.75 ± 1.32, P = 0.001; 4.20 ± 2.21 vs 0.75 ± 1.32, P < 0.001, respectively) and, healthy volunteers (4.67 ± 2.42 vs 0.67 ± 1.46, P = 0.001; 4.20 ± 2.21 vs 0.67 ± 1.46, P = 0.001, respectively). Vomiting was referred in 100% of bulimia nervosa patients, in 20% of ED not otherwise specified patients, in 15% of anorexia nervosa patients, in 22% of constitutional thinner subjects, and, in 5.6% healthy volunteers (χ(2), P < 0.001).
Conclusion: PDS is common in eating disorders. Is it mandatory in outpatient gastroenterological clinics to investigate eating disorders in patients with PDS?
Keywords: Anorexia nervosa; Bulimia nervosa; Constitutional thinness; Eating disorders; Eating disorders not otherwise specified; Epigastric pain sindrome; Functional dyspepsia; Post prandial distress syndrome; Rome III criteria; Upper abdominal symptoms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathophysiological Abnormalities in Functional Dyspepsia Subgroups According to the Rome III Criteria.Am J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jan;112(1):132-140. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2016.499. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 27958284
-
Anhedonia and functional dyspepsia in obese patients: Relationship with binge eating behaviour.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 May 28;26(20):2632-2644. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i20.2632. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32523316 Free PMC article.
-
Symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) among adult eating disorder patients.BMC Psychiatry. 2017 Jan 17;17(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12888-016-1093-1. BMC Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28095885 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring health-related quality of life in eating disorders by a cross-sectional study and a comprehensive review.BMC Psychiatry. 2014 Jun 4;14:165. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-14-165. BMC Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24898768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Eating disorders - diagnosis and characteristics].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2020 Apr 22;48(284):133-138. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2020. PMID: 32352948 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Assessment of proximal gastric accommodation in patients with functional dyspepsia.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Dec 21;19(47):9137-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9137. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24379642 Free PMC article.
-
European Guideline on Chronic Nausea and Vomiting-A UEG and ESNM Consensus for Clinical Management.United European Gastroenterol J. 2025 Apr;13(3):427-471. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12711. Epub 2025 Jan 4. United European Gastroenterol J. 2025. PMID: 39754724 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal vests help patients with anorexia nervosa to cope with mealtime anxiety.J Eat Disord. 2025 Jul 28;13(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s40337-025-01324-9. J Eat Disord. 2025. PMID: 40722042 Free PMC article.
-
Food Allergy and Intolerance: A Narrative Review on Nutritional Concerns.Nutrients. 2021 May 13;13(5):1638. doi: 10.3390/nu13051638. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34068047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bloating and functional gastro-intestinal disorders: where are we and where are we going?World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 21;20(39):14407-19. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14407. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25339827 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lewinsohn PM, Hops H, Roberts RE, Seeley JR, Andrews JA. Adolescent psychopathology: I. Prevalence and incidence of depression and other DSM-III-R disorders in high school students. J Abnorm Psychol. 1993;102:133–144. - PubMed
-
- Fairburn CG, Harrison PJ. Eating disorders. Lancet. 2003;361:407–416. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
-
- Boyd C, Abraham S, Kellow J. Psychological features are important predictors of functional gastrointestinal disorders in patients with eating disorders. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:929–935. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

