Efficacy of a therapeutic strategy for eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection
- PMID: 22969227
- PMCID: PMC3435779
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i33.4542
Efficacy of a therapeutic strategy for eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection
Abstract
Aim: To determine the efficacy of our therapeutic strategy for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication and to identify predictive factors for successful eradication.
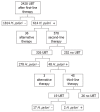
Methods: From April 2006 to June 2010, we retrospectively assessed 2428 consecutive patients (1025 men, 1403 women; mean age 55 years, age range 18-92 years) with gastric histology positive for H. pylori infection referred to our unit for 13-C urea breath test (UBT), after first-line therapy with proton pump inhibitor (PPI) b.i.d. + amoxicillin 1 g b.i.d. + clarithromycin 500 mg b.i.d. for 7 d. Patients who were still positive to UBT were recommended a second-line therapy (PPI b.i.d. + amoxicillin 1 g b.i.d. + tinidazole 500 mg b.i.d. for 14 d). Third choice treatment was empirical with PPI b.i.d. + amoxicillin 1 g b.i.d. + levofloxacin 250 mg b.i.d. for 14 d.
Results: Out of 614 patients, still H. pylori-positive after first-line therapy, only 326 and 19 patients respectively rechecked their H. pylori status by UBT after the suggested second and third-line regimens. "Per protocol" eradication rates for first, second and third-line therapy were 74.7% (95% CI: 72.7%-76.4%), 85.3% (95% CI: 81.1%-89.1%) and 89.5% (95% CI: 74.9%-103%) respectively. The overall percentage of patients with H. pylori eradicated after two treatments was 97.8% (95% CI: 97.1%-98.4%), vs 99.9% (95% CI: 99.8%-100%) after three treatments. The study found that eradication therapy was most effective in patients with ulcer disease (P < 0.05, P = 0.028), especially in those with duodenal ulcer. Smoking habits did not significantly affect the eradication rate.
Conclusion: First-line therapy with amoxicillin and clarithromycin produces an H. pylori eradication rate comparable or superior to other studies and second-line treatment can still be triple therapy with amoxicillin and tinidazole.
Keywords: Eradication rate; Eradication treatment; First-line therapy; Helicobacter pylori; Rescue therapy; Second-line therapy; Triple therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Marshall B. Helicobacter pylori Research Laboratory. Available from: http//www.hpylori.com.au/
-
- World Gastroenterology Organisation. World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guideline: Helicobacter pylori in developing countries. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011;45:383–388. - PubMed
-
- Wotherspoon AC, Doglioni C, Diss TC, Pan L, Moschini A, de Boni M, Isaacson PG. Regression of primary low-grade B-cell gastric lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet. 1993;342:575–577. - PubMed
-
- Bertoni F, Coiffier B, Salles G, Stathis A, Traverse-Glehen A, Thieblemont C, Zucca E. MALT lymphomas: pathogenesis can drive treatment. Oncology (Williston Park) 2011;25:1134–1142, 1147. - PubMed
-
- Fiocca R, Luinetti L, Villani L, Chiaravalli A, Cornaggia M, Stella G, Perego M, Trespi E, Solcia E. High incidence of Helicobacter pylori colonization in early gastric cancer and the possible relationship to carcinogenesis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1993;5:S2–S8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous