The time between paraquat ingestion and a negative dithionite urine test in an independent risk factor for death and organ failure in acute paraquat intoxication
- PMID: 22969243
- PMCID: PMC3429840
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.9.993
The time between paraquat ingestion and a negative dithionite urine test in an independent risk factor for death and organ failure in acute paraquat intoxication
Abstract
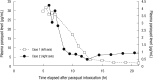
To identify a prognostic marker that is less sensitive to variations in the elapsed time since paraquat ingestion, we assessed the time between paraquat ingestion and a negative dithionite urine test as a prognostic parameter in patients with acute paraquat intoxication. Forty-one patients with acute paraquat intoxication were enrolled in this study and analyzed to verify significant determinants of mortality and organ dysfunction. The amount of paraquat ingested, paraquat plasma levels, and the time to a negative urine dithionite test were significant independent risk factors predicting mortality. The amount of paraquat ingestion, and the time to a negative urine dithionite test were independent risk factors predicting organ dysfunction. With a cut-off value of 34.5 hr for the time to negative conversion of the urine dithionite test, the sensitivity and specificity for mortality were 71.4% and 75.0%, respectively. The incidence of acute kidney injury and respiratory failure above 34.5 hr were 100% and 85.0%, respectively. In conclusion, the time to a negative urine dithionite test is the reliable marker for predicting mortality and/or essential organ failure in patients with acute paraquat intoxication, who survive 72 hr.
Keywords: Dithionite Test; Intoxication; Mortality; Multiple Organ Failure; Paraquat; Risk Factors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rapid analysis of plasma paraquat using sodium dithionite as a predictor of outcome in acute paraquat poisoning.Am J Med Sci. 2009 Nov;338(5):373-7. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3181b4deee. Am J Med Sci. 2009. PMID: 19826241
-
Serum uric acid level as a marker for mortality and acute kidney injury in patients with acute paraquat intoxication.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011 Jun;26(6):1846-52. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfq632. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011. PMID: 20966188
-
[Analysis of risk factors for prognosis of patients with acute paraquat intoxication].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Nov;27(11):906-10. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 27132458 Chinese.
-
Diagnostic and therapeutic approach for acute paraquat intoxication.J Korean Med Sci. 2014 Nov;29(11):1441-9. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.11.1441. Epub 2014 Nov 4. J Korean Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 25408572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Point-of-care testing in the early diagnosis of acute pesticide intoxication: The example of paraquat.Biomicrofluidics. 2018 Jan 19;12(1):011501. doi: 10.1063/1.5003848. eCollection 2018 Jan. Biomicrofluidics. 2018. PMID: 29430271 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Features, Treatment, Prognosis, and Mortality in Paraquat Poisonings: A Hospital-Based Study in Iran.J Res Pharm Pract. 2019 Oct 16;8(3):129-136. doi: 10.4103/jrpp.JRPP_18_71. eCollection 2019 Jul-Sep. J Res Pharm Pract. 2019. PMID: 31728343 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of gastric lavage efficiency and utility using a rapid quantitative method in a swine paraquat poisoning model.World J Emerg Med. 2020;11(3):174-181. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2020.03.008. World J Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 32351651 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of severity index and plasma paraquat concentration for predicting survival after paraquat poisoning: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Feb;99(6):e19063. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019063. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32028427 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive values of urine paraquat concentration, dose of poison, arterial blood lactate and APACHE II score in the prognosis of patients with acute paraquat poisoning.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Jul;14(1):79-86. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4463. Epub 2017 May 17. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28672896 Free PMC article.
-
Hypokalemia is a biochemical signal of poor prognosis for acute paraquat poisoning within 4 hours.Intern Emerg Med. 2017 Sep;12(6):837-843. doi: 10.1007/s11739-016-1491-x. Epub 2016 Jul 9. Intern Emerg Med. 2017. PMID: 27395362
References
-
- Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Chen KH, Huang WH, Hsu CW, Hsu HH, Yen TH. Improved survival in severe paraquat poisoning with repeated pulse therapy of cyclophosphamide and steroids. Intensive Care Med. 2011;37:1006–1013. - PubMed
-
- Moon JM, Chun BJ. The efficacy of high doses of vitamin C in patients with paraquat poisoning. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2011;30:844–850. - PubMed
-
- Gil HW, Kim SJ, Yang JO, Lee EY, Hong SY. Clinical outcome of hemoperfusion in poisoned patients. Blood Purif. 2010;30:84–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

