Oncogenic microRNA 17-92 cluster is regulated by epithelial cell adhesion molecule and could be a potential therapeutic target in retinoblastoma
- PMID: 22969266
- PMCID: PMC3436882
Oncogenic microRNA 17-92 cluster is regulated by epithelial cell adhesion molecule and could be a potential therapeutic target in retinoblastoma
Abstract
Purpose: Several miRNAs have been reported as candidate oncogenes and tumor suppressors, which are involved in the pathways specifically altered during tumorigenesis or metastasis. The miR 17-92 cluster located in 13q31 locus might contribute to retinoblastoma (RB) oncogenesis as 13q31 is amplified often in RB. We attempted to identify the factors involved in the regulation of miR 17-92 cluster in RB.
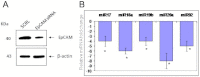
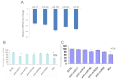
Methods: Real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR was performed to study the expression of the miR 17-92 cluster in primary RB tumors and in Y79 cells after epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) silencing. EpCAM was silenced using siRNA and confirmed by western blotting. The Y79 cells were transfected with individual and mixed antagomirs and studied the cell viability by (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, invasion by matrigel analysis and caspase-3 expression by flow cytometry.
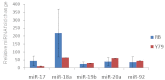
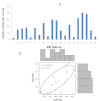
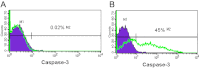
Results: The relative expression of miR 17-92 cluster, compared to that of a normal retina, ranged from 25 to 220 fold (p<0.0001), miR-18 being highly expressed in RB. Post EpCAM silencing resulted in a significant decrease (p<0.01) in the expression of the miR 17-92 cluster by 4 to eightfold in Y79 cells. Y79 cells transfected with an antagomirs mix (all 5 miRNAs) showed decreased cell viability (p<0.001) and cell invasion (p<0.001). Similarly, Y79 cells treated with antagomirs mix showed increased expression of caspase-3 (p<0.001), which confirms the anti-proliferative effect of antagomirs.
Conclusions: This study has showed varied expression of the miR17-92 cluster in primary RB tumors. EpCAM influences miR 17-92 cluster expression in retinoblastoma. In addition, we showed that the miR 17-92 cluster plays a role in RB cell proliferation and invasion. Therefore, targeting the miRNA 17-92 cluster may be beneficial for controlling Y79/RB cell proliferation and invasion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EpCAM knockdown alters microRNA expression in retinoblastoma--functional implication of EpCAM regulated miRNA in tumor progression.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 12;9(12):e114800. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114800. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25502397 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of curcumin on miRNA expression in human Y79 retinoblastoma cells.Curr Eye Res. 2012 May;37(5):421-8. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2011.647224. Curr Eye Res. 2012. PMID: 22510010
-
EpCAM is a putative stem marker in retinoblastoma and an effective target for T-cell-mediated immunotherapy.Mol Vis. 2012;18:290-308. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Mol Vis. 2012. PMID: 22328825 Free PMC article.
-
EpCAM and its potential role in tumor-initiating cells.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 Jan-Feb;6(1):30-8. doi: 10.4161/cam.18953. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 22647938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs' Significance in Retinoblastoma Diagnosis and Treatment: The Little Heroes.Biochem Genet. 2025 Apr;63(2):1176-1197. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10976-2. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 39862293 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Chemoresistance in Advanced Retinoblastoma Tumors Is Driven by miR-181a.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 19;14(20):5124. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205124. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291907 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the lipid metabolic axis ACSL/SCD in colorectal cancer progression by therapeutic miRNAs: miR-19b-1 role.J Lipid Res. 2018 Jan;59(1):14-24. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M076752. Epub 2017 Oct 26. J Lipid Res. 2018. PMID: 29074607 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of microRNA gene regulation on the survival and function of mature cell types in the eye.FASEB J. 2016 Jan;30(1):23-33. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-279745. Epub 2015 Sep 23. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26399786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EpCAM Aptamer-siRNA Chimera Targets and Regress Epithelial Cancer.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0132407. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132407. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26176230 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrations in Angiogenic Signaling and MYC Amplifications are Distinguishing Features of Angiosarcoma.Angiol Open Access. 2013 Apr 8;1:17309. doi: 10.4172/2329-9495.1000102. Angiol Open Access. 2013. PMID: 25374893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA-cancer connection: the beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 2006;66:7390–4. - PubMed
-
- Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R, Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, Sharon E, Spector Y, Bentwich Z. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet. 2005;37:766–70. - PubMed
-
- Zamore PD, Haley B. Ribo-gnome: the big world of small RNAs. Science. 2005;309:1519–24. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-ranscriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:102–14. - PubMed
-
- Stefani G, Slack FJ. Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:219–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
