Clade age and species richness are decoupled across the eukaryotic tree of life
- PMID: 22969411
- PMCID: PMC3433737
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001381
Clade age and species richness are decoupled across the eukaryotic tree of life
Abstract
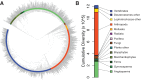
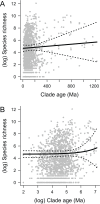
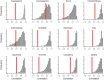
Explaining the dramatic variation in species richness across the tree of life remains a key challenge in evolutionary biology. At the largest phylogenetic scales, the extreme heterogeneity in species richness observed among different groups of organisms is almost certainly a function of many complex and interdependent factors. However, the most fundamental expectation in macroevolutionary studies is simply that species richness in extant clades should be correlated with clade age: all things being equal, older clades will have had more time for diversity to accumulate than younger clades. Here, we test the relationship between stem clade age and species richness across 1,397 major clades of multicellular eukaryotes that collectively account for more than 1.2 million described species. We find no evidence that clade age predicts species richness at this scale. We demonstrate that this decoupling of age and richness is unlikely to result from variation in net diversification rates among clades. At the largest phylogenetic scales, contemporary patterns of species richness are inconsistent with unbounded diversity increase through time. These results imply that a fundamentally different interpretative paradigm may be needed in the study of phylogenetic diversity patterns in many groups of organisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Comment in
-
An inordinate fondness for eukaryotic diversity.PLoS Biol. 2012 Aug;10(8):e1001382. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001382. Epub 2012 Aug 28. PLoS Biol. 2012. PMID: 22952431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raup DM, Gould SJ, Schopf TJM, Simberloff D (1973) Stochastic models of phylogeny and evolution of diversity. J Geol 81: 525–542.

