Real-time transcriptional profiling of cellular and viral gene expression during lytic cytomegalovirus infection
- PMID: 22969428
- PMCID: PMC3435240
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002908
Real-time transcriptional profiling of cellular and viral gene expression during lytic cytomegalovirus infection
Abstract
During viral infections cellular gene expression is subject to rapid alterations induced by both viral and antiviral mechanisms. In this study, we applied metabolic labeling of newly transcribed RNA with 4-thiouridine (4sU-tagging) to dissect the real-time kinetics of cellular and viral transcriptional activity during lytic murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) infection. Microarray profiling on newly transcribed RNA obtained at different times during the first six hours of MCMV infection revealed discrete functional clusters of cellular genes regulated with distinct kinetics at surprising temporal resolution. Immediately upon virus entry, a cluster of NF-κB- and interferon-regulated genes was induced. Rapid viral counter-regulation of this coincided with a very transient DNA-damage response, followed by a delayed ER-stress response. Rapid counter-regulation of all three clusters indicated the involvement of novel viral regulators targeting these pathways. In addition, down-regulation of two clusters involved in cell-differentiation (rapid repression) and cell-cycle (delayed repression) was observed. Promoter analysis revealed all five clusters to be associated with distinct transcription factors, of which NF-κB and c-Myc were validated to precisely match the respective transcriptional changes observed in newly transcribed RNA. 4sU-tagging also allowed us to study the real-time kinetics of viral gene expression in the absence of any interfering virion-associated-RNA. Both qRT-PCR and next-generation sequencing demonstrated a sharp peak of viral gene expression during the first two hours of infection including transcription of immediate-early, early and even well characterized late genes. Interestingly, this was subject to rapid gene silencing by 5-6 hours post infection. Despite the rapid increase in viral DNA load during viral DNA replication, transcriptional activity of some viral genes remained remarkably constant until late-stage infection, or was subject to further continuous decline. In summary, this study pioneers real-time transcriptional analysis during a lytic herpesvirus infection and highlights numerous novel regulatory aspects of virus-host-cell interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
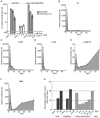
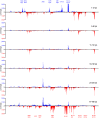
References
-
- Mocarski E, Shenk T, Pass R (2007) Cytomegaloviruses. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors Fields Virology, Vol2, pp 2701–2772 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia.
-
- Compton T, Feire A (2007) Early events in human cytomegalovirus infection. In: Source Human Herpesviruses: Biology, Therapy, and Immunoprophylaxis. Arvin A, Campadelli-Fiume G, Mocarski E, Moore PS, Roizman B, Whitley R, Yamanishi K, editors. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Chapter 16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

