A core circuit module for cost/benefit decision
- PMID: 22969700
- PMCID: PMC3431595
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00123
A core circuit module for cost/benefit decision
Abstract
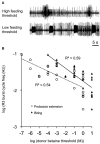
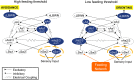
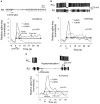
A simple circuit for cost-benefit decision derived from behavioral and neural studies of the predatory sea-slug Pleurobranchaea may closely resemble that upon which the more complex valuation and decision processes of the social vertebrates are built. The neuronal natures of the pathways in the connectionist model comprise classic central pattern generators, bipolar switch mechanisms, and neuromodulatory state regulation. Marked potential exists for exploring more complex neuroeconomic behavior by appending appropriate circuitry in simulo.
Keywords: Pleurobranchaea; approach/avoidance; central pattern generator; decision making; neuroeconomics; neuronal switch; simulation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Sea Slug, Pleurobranchaea californica: A Signpost Species in the Evolution of Complex Nervous Systems and Behavior.Integr Comp Biol. 2015 Dec;55(6):1058-69. doi: 10.1093/icb/icv081. Epub 2015 Jul 10. Integr Comp Biol. 2015. PMID: 26163678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implementing Goal-Directed Foraging Decisions of a Simpler Nervous System in Simulation.eNeuro. 2018 Mar 1;5(1):ENEURO.0400-17.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0400-17.2018. eCollection 2018 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 29503862 Free PMC article.
-
A neuronal network switch for approach/avoidance toggled by appetitive state.Curr Biol. 2012 Jan 24;22(2):118-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.10.055. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22197246 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromodulatory control of a goal-directed decision.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 21;9(7):e102240. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102240. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25048964 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroeconomics and the study of addiction.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Jul 15;72(2):107-12. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.03.012. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22520343 Review.
Cited by
-
Selection of motor programs for suppressing food intake and inducing locomotion in the Drosophila brain.PLoS Biol. 2014 Jun 24;12(6):e1001893. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001893. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2014. PMID: 24960360 Free PMC article.
-
The Sea Slug, Pleurobranchaea californica: A Signpost Species in the Evolution of Complex Nervous Systems and Behavior.Integr Comp Biol. 2015 Dec;55(6):1058-69. doi: 10.1093/icb/icv081. Epub 2015 Jul 10. Integr Comp Biol. 2015. PMID: 26163678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A common modular design of nervous systems originating in soft-bodied invertebrates.Front Physiol. 2023 Oct 3;14:1263453. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1263453. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37854468 Free PMC article.
-
Invertebrate behavior-actions or responses?Front Neurosci. 2013 Nov 19;7:221. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00221. eCollection 2013. Front Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24311998 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Implementing Goal-Directed Foraging Decisions of a Simpler Nervous System in Simulation.eNeuro. 2018 Mar 1;5(1):ENEURO.0400-17.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0400-17.2018. eCollection 2018 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 29503862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bicker G., Davis W. J., Matera E. M., Kovac M. P., Stormo Gipson D. J. (1982a). Chemoreception and mechanoreception in the gastropod mollusc Pleurobranchaea californica. I. Extracellular analysis of afferent pathways. J. Comp. Physiol. 149, 221–23410.1007/BF00619217 - DOI
-
- Bicker G., Davis W. J., Matera E. (1982b). Chemoreception and mechanoreception in the gastropod mollusc Pleurobranchaea californica. II. Neuroanatomical and intracellular analysis of afferent pathways. J. Comp. Physiol. 149, 235–25010.1007/BF00619217 - DOI
-
- Davis W. J., Mpitsos G. J. (1971). Behavioral choice and habituation in the marine mollusk Pleurobranchaea californica. Z. Vergl. Physiol. 75, 207–232
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

