Chromatinized Protein Kinase C-θ: Can It Escape the Clutches of NF-κB?
- PMID: 22969762
- PMCID: PMC3428636
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00260
Chromatinized Protein Kinase C-θ: Can It Escape the Clutches of NF-κB?
Abstract
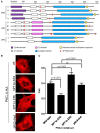
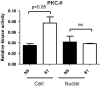
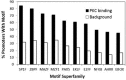
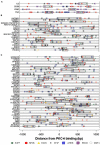
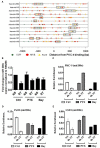
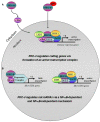
We recently provided the first description of a nuclear mechanism used by Protein Kinase C-theta (PKC-θ) to mediate T cell gene expression. In this mode, PKC-θ tethers to chromatin to form an active nuclear complex by interacting with proteins including RNA polymerase II, the histone kinase MSK-1, the demethylase LSD1, and the adaptor molecule 14-3-3ζ at regulatory regions of inducible immune response genes. Moreover, our genome-wide analysis identified many novel PKC-θ target genes and microRNAs implicated in T cell development, differentiation, apoptosis, and proliferation. We have expanded our ChIP-on-chip analysis and have now identified a transcription factor motif containing NF-κB binding sites that may facilitate recruitment of PKC-θ to chromatin at coding genes. Furthermore, NF-κB association with chromatin appears to be a prerequisite for the assembly of the PKC-θ active complex. In contrast, a distinct NF-κB-containing module appears to operate at PKC-θ targeted microRNA genes, and here NF-κB negatively regulates microRNA gene transcription. Our efforts are also focusing on distinguishing between the nuclear and cytoplasmic functions of PKCs to ascertain how these kinases may synergize their roles as both cytoplasmic signaling proteins and their functions on the chromatin template, together enabling rapid induction of eukaryotic genes. We have identified an alternative sequence within PKC-θ that appears to be important for nuclear translocation of this kinase. Understanding the molecular mechanisms used by signal transduction kinases to elicit specific and distinct transcriptional programs in T cells will enable scientists to refine current therapeutic strategies for autoimmune diseases and cancer.
Keywords: NF-κB; PKC-theta; T cells; chromatin; immune response gene; microRNA; nuclear PKC-theta; signaling kinase.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

