microRNA-99b acts as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer by directly targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 3
- PMID: 22969861
- PMCID: PMC3438617
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2011.366
microRNA-99b acts as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer by directly targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 3
Abstract
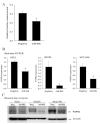
microRNAs (miRNAs) play a significant role in cancer development and progression by regulating the expression of proto-oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes. Our previous study using microarrays demonstrated that miR-99b was downregulated in patients with lung cancer. To assess whether or not miR-99b has a functional role in lung cancer, we determined the expression of miR-99b and fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3), which is a predicted target of miR-99b in public algorithms in human lung cancer tissues. miR-99b was downregulated and FGFR3 was upregulated in lung cancer patients. We demonstrated that the overexpression of miR-99b induced a reduction in FGFR3 expression and confirmed the target specificity between miR-99b and the FGFR3 3'-untranslated region by luciferase reporter assay. In addition, the growth rate in miR-99b precursor-treated cells was lower compared to the negative controls. Taken together, these results suggest that miR-99b may be a tumor suppressor through the downregulation of FGFR3. miR-99b may be a potent tumor suppressor and may be a potential therapeutic tool for patients with lung cancer.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nicotine upregulates FGFR3 and RB1 expression and promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via downregulation of miR-99b and miR-192.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 May;101:656-662. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.113. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29518612
-
MiR-99b-5p suppressed proliferation of human osteoblasts by targeting FGFR3 in osteoporosis.Hum Cell. 2021 Sep;34(5):1398-1409. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00567-3. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 34156640
-
Exosomal miR-99b-5p Secreted from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Can Retard the Progression of Colorectal Cancer by Targeting FGFR3.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 Nov;19(8):2901-2917. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10606-1. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 37653181
-
MiR-142-3p functions as a potential tumor suppressor directly targeting HMGB1 in non-small-cell lung carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Sep 1;8(9):10800-7. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26617792 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-99b-5p suppresses liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by down-regulating mTOR.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 15;6(27):24448-62. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4423. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26259252 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulation of IGF -1 signaling by microRNAs.Front Genet. 2015 Jan 13;5:472. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00472. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25628647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-613 inhibits cell growth, migration and invasion of papillary thyroid carcinoma by regulating SphK2.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 28;7(26):39907-39915. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9530. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27223438 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of microRNA-99 family in human glioma.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Jun 20;9:3613-9. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S99363. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27382299 Free PMC article.
-
miR-641 Functions as a Tumor Suppressor by Targeting MDM2 in Human Lung Cancer.Oncol Res. 2018 Jun 11;26(5):735-741. doi: 10.3727/096504017X15021536183490. Epub 2017 Aug 11. Oncol Res. 2018. Retraction in: Oncol Res. 2025 Feb 28;33(3):737. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.056910. PMID: 28800790 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The tumorigenic FGFR3-TACC3 gene fusion escapes miR-99a regulation in glioblastoma.J Clin Invest. 2013 Feb;123(2):855-65. doi: 10.1172/JCI67144. Epub 2013 Jan 9. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23298836 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
