CHOP and caspase 3 induction underlie glioblastoma cell death in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 22969916
- PMCID: PMC3438596
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2011.422
CHOP and caspase 3 induction underlie glioblastoma cell death in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
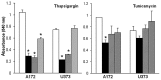
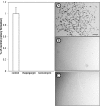
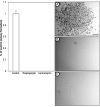
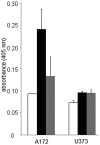
The unfolded protein endoplasmic reticulum stress response has emerged as a cellular physiological target to invoke tumor cell killing due to its homeostatic and cytoprotective functions. In this study, thapsigargin and tunicamycin, two endoplasmic reticulum stress inducers, were investigated for their efficacy on glioblastomas. We demonstrate that clinically relevant concentrations of thapsigargin and tunicamycin eliminate the glioblastoma cell reproductive capacity as a consequence of cell death. The mode of glioblastoma-induced cell death was determined to be via apoptosis as supported by increased C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) levels and caspase 3 activity, two proteins with established roles in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death. In conclusion, this study provides evidence that glioblastomas are responsive to endoplasmic reticulum stress induction as a cellular program to eradicate this tumor via programmed cell death.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Caspase-11 mediates ischemia-induced astrocyte death: involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress and C/EBP homologous protein.J Neurosci Res. 2010 Apr;88(5):1094-105. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22280. J Neurosci Res. 2010. PMID: 19890920
-
Ghrelin suppresses tunicamycin- or thapsigargin-triggered endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in primary cultured rat cortical neuronal cells.Endocr J. 2011;58(5):409-20. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.k10e-396. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Endocr J. 2011. PMID: 21490406
-
Neuronal apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress is regulated by ATF4-CHOP-mediated induction of the Bcl-2 homology 3-only member PUMA.J Neurosci. 2010 Dec 15;30(50):16938-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1598-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21159964 Free PMC article.
-
The C/EBP Homologous Protein (CHOP) Transcription Factor Functions in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Microbial Infection.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 4;9:3083. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03083. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30662442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress.FEBS J. 2016 Jul;283(14):2640-52. doi: 10.1111/febs.13598. Epub 2015 Dec 19. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26587781 Review.
Cited by
-
Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Protects Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells from Oxidative Injury and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress In Vitro.Biomedicines. 2020 Sep 21;8(9):367. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8090367. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32967221 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol Uses Different Mechanisms in Astrocytes from the Hippocampus of Male and Female Rats to Protect against Damage Induced by Palmitic Acid.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Oct 24;10:330. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00330. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29114202 Free PMC article.
-
Smyd1 facilitates heart development by antagonizing oxidative and ER stress responses.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 24;10(3):e0121765. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121765. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25803368 Free PMC article.
-
Activating transcription factor 4 underlies the pathogenesis of arsenic trioxide-mediated impairment of macrophage innate immune functions.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 Oct 1;308:46-58. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.07.015. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27461142 Free PMC article.
-
Seawater inhalation induces acute lung injury via ROS generation and the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2018 May;41(5):2505-2516. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3486. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29436612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kögel D, Fulda S, Mittelbronn M. Therapeutic exploitation of apoptosis and autophagy for glioblastoma. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2010;10:438–449. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
