LNA real-time PCR probe quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA
- PMID: 22969919
- PMCID: PMC3438541
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2011.442
LNA real-time PCR probe quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA
Abstract
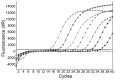
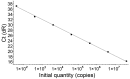
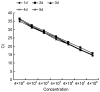
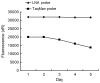
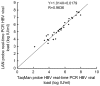
In the present study, we standardized a TaqMan locked nucleic acid (LNA) real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) probe for the accurate quantification and detection of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA in serum (plasma), and evaluated its methodology. LNA probe technology had a much better detection performance in HBV DNA than the common TaqMan probe. The assay based on the LNA probe had a wider linear detection range, higher sensitivity, stability and amplification efficiency, and a lower concentration of probes than the TaqMan probe. Among the 15 cases with chronic hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) (+) alone, only 4 cases that were detected by TaqMan real-time PCR were negative; however, the same samples were positive by LNA real-time PCR (p<0.05). A positive correlation between viral load measurements for the 35 samples with HBV-positive DNA was detected in both LNA and TaqMan real-time PCR.
Figures
References
-
- Schalm SW. Treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Neth J Med. 1994;44:103–109. - PubMed
-
- Jardi R, Buti M, Rodriguez-Frias F, et al. The value of quantitative detection of HBV-DNA amplified by PCR in the study of hepatitis B infection. J Hepatol. 1996;24:680–685. - PubMed
-
- Berger A, Braner J, Doerr HW, Weber B. Quantification of viral load: clinical relevance for human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Intervirology. 1998;41:24–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
