Aspirin upregulates the expression of neuregulin 1 and survivin after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats
- PMID: 22969938
- PMCID: PMC3438529
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2012.450
Aspirin upregulates the expression of neuregulin 1 and survivin after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats
Abstract
Neuregulin 1 (NGR1) and survivin have been shown to be neuroprotective. However, the link between their expression and aspirin in the treatment of cerebral ischemia remains unclear. Here, we investigated the effect of aspirin on NGR1 and survivin expression after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Sprague Dawley rats were randomly divided into an aspirin treatment group (n=40) and a control group (n=40). Each group was further divided into five subgroups according to the time after reperfusion. A middle cerebral artery model was established by an occlusion suture. At 24 h, 3, 5 and 7 days after reperfusion, the Bederson neurological deficit scores were 1.47±0.11, 1.22±0.08, 0.85±0.15 and 0.59±0.12 in the treatment group, and 1.87±0.18, 1.45±0.14, 1.05±0.08 and 0.75±0.15 in the control group, respectively, indicating a significant difference at each time point (P<0.05). In the infarct center, the number of NGR1- and survivin-positive cells reached the maximum at 6 h and decreased gradually to a minimum at 7 days, while in the peri-infarct area, the number was few at 6 h, peaked at 3 days and then was reduced gradually with significant differences between the two time points (P<0.05). There were more NGR1- and survivin-positive cells in the treatment group compared to the control group (P<0.05). In conclusion, the neuroprotective effect of aspirin is at least partly mediated by the upregulation of NGR1 and survivin expression after ischemia.
Figures
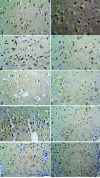
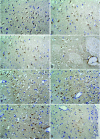
References
-
- Guo WP, Wang J, Li RX, Peng YW. Neuroprotective effects of neuregulin-1 in rat models of focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2006;1087:180–185. - PubMed
-
- Li Q, Li Z, Mei Y, Guo Y. Neuregulin attenuated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibiting apoptosis and upregulating aquaporin-4. Neurosci Lett. 2008;443:155–159. - PubMed
-
- Li Q, Zhang R, Guo YL, Mei YW. Effect of neuregulin on apoptosis and expressions of STAT3 and GFAP in rats following cerebral ischemic reperfusion. J Mol Neurosci. 2009;37:67–73. - PubMed
-
- Shyu WC, Lin SZ, Chiang MF, Yang HI, Thajeb P, Li H. Neuregulin-1 reduces ischemia-induced brain damage in rats. Neurobiol Aging. 2004;25:935–944. - PubMed
-
- Xu Z, Croslan DR, Harris AE, Ford GD, Ford BD. Extended therapeutic window and functional recovery after intraarterial administration of neuregulin-1 after focal ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26:527–535. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
