Connective tissue growth factor gene expression and decline in renal function in lupus nephritis
- PMID: 22969957
- PMCID: PMC3438605
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2012.473
Connective tissue growth factor gene expression and decline in renal function in lupus nephritis
Abstract
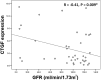
In lupus nephritis (LN), kidney inflammation may be followed by fibrosis and progressive decline in function. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β is a notable mediator of fibrosis, but it has other beneficial roles, thus indicating a need for alternate therapeutic targets for inhibition of fibrosis. Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) acts as a downstream mediator of TGF-β in promoting fibrosis, without mediating the immunosuppressive effects of TGF-β. Animal studies show that CTGF may have important roles in renal fibrosis, but data are limited in human subjects. The present study tested the hypothesis that renal CTGF mRNA expression is related to TGF-β1 and collagen I expression and is predictive of renal function deterioration in patients with LN (n=39). Gene expression was measured using multiplex real-time quantitative RT-PCR and renal function was estimated using the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) glomerular filtration rate (GFR) equation. Decline in GFR was assessed by regression of GFR at biopsy to 1 year following biopsy. CTGF mRNA expression was significantly correlated with TGF-β1 and collagen I. GFR at biopsy was 89.2±39.2 ml/ min. Renal CTGF mRNA expression correlated inversely with baseline GFR. Renal CTGF mRNA was significantly higher in patients with moderate to severe CKD compared to those in the milder CKD group (low GFR 4.92±4.34 vs. high GFR 1.52±1.94, p<0.005). CTGF mRNA was also higher in patients with subsequent decline in GFR [GFR decline (5.19±4.46) vs. no GFR decline (1.79±1.97); P<0.01]. In conclusion, renal expression of CTGF was positively related to TGF-β1 and collagen I in patients with LN. Furthermore, high CTGF mRNA expression was associated with poor GFR at baseline and subsequent deterioration of kidney function. CTGF expression in the kidney may serve as an early marker for renal disease progression and could be evaluated as a target for therapeutic intervention to prevent renal failure in LN.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Glomerular Expression of Some Profibrotic Factors in Progressive Childhood Lupus Nephritis.J Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Dec;26(8):305-312. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000001118. J Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31356397
-
Role of connective tissue growth factor in the pathogenesis of conjunctival scarring in ocular cicatricial pemphigoid.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 May;44(5):1998-2003. doi: 10.1167/iovs.02-0967. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. PMID: 12714635
-
Renal mRNA levels as prognostic tools in kidney diseases.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003 Apr;14(4):899-907. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000056611.92730.7b. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003. PMID: 12660324
-
Connective Tissue Growth Factor and Renal Fibrosis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1165:365-380. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-8871-2_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31399974 Review.
-
Central role of dysregulation of TGF-β/Smad in CKD progression and potential targets of its treatment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 May;101:670-681. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.090. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29518614 Review.
Cited by
-
CTGF in kidney fibrosis and glomerulonephritis.Inflamm Regen. 2018 Aug 6;38:14. doi: 10.1186/s41232-018-0070-0. eCollection 2018. Inflamm Regen. 2018. PMID: 30123390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study on Connective Tissue Growth Factor Expressed in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2019 Jul;35(4):355-359. doi: 10.6515/ACS.201907_35(4).20180922A. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2019. PMID: 31371895 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of appropriate reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in a streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer's disease model of cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis).PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056034. Epub 2013 Feb 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23457495 Free PMC article.
-
Trichostatin A inhibits radiation-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the alveolar epithelial cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 9;8(60):101745-101759. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21664. eCollection 2017 Nov 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29254201 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Bu-Shen-Huo-Xue Formula against 5/6 Nephrectomy-Induced Chronic Renal Failure in Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:589846. doi: 10.1155/2014/589846. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 24864155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D'Cruz DP, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 2007;17:587–596. - PubMed
-
- Markowitz GS, D'Agati VD. Classification of lupus nephritis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2009;18:220–225. - PubMed
-
- Boor P, Ostendorf T, Floege J. Renal fibrosis: novel insights into mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010;6:643–656. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Sanchez O, Lopez-Hernandez FJ, Lopez-Novoa JM. An integrative view on the role of TGF-beta in the progressive tubular deletion associated with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2010;77:950–955. - PubMed
-
- Zeisberg M, Neilson EG. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:1819–1834. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
