Combination therapy using oral S-1 and targeted agents against human tumor xenografts in nude mice
- PMID: 22969964
- PMCID: PMC3438730
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2012.484
Combination therapy using oral S-1 and targeted agents against human tumor xenografts in nude mice
Abstract
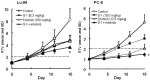
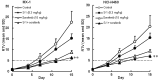
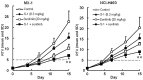
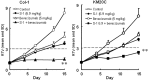
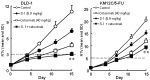
In this study, combination therapies using the oral fluoropyrimidine tegafur-gimeracil-oteracil (S-1) with several targeted agents or antibodies, were evaluated. First, the effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (erlotinib hydrochloride, sorafenib tosilate and sunitinib malate) against human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), breast cancer and colorectal cancer were evaluated in vivo. The effects of the combination of S-1 and targeted antibodies (bevacizumab and cetuximab) against human colorectal cancers was also evaluated in vivo. S-1 and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, erlotinib, showed a significant inhibition of growth in human NSCLC (Lu-99 and PC-9 cell lines). The antitumor activity of the combination of S-1 and erlotinib against Lu-99 and PC-9 cancer cell lines was significantly superior to either monotherapy (P<0.05). Combination therapy using the multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitors, sorafenib or sunitinib, with S-1 against breast cancer (MX-1 cell line) and NSCLC (NCI-H460 cell line) was significantly superior to either monotherapy (P<0.01). The combination of the anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody bevacizumab or the anti-EGFR antibody, cetuximab, with S-1 against human colorectal cancer [Col-1, KM20C (bevacizumab) and DLD-1 (cetuximab) cell lines] and a 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)-resistant cell line (KM12C/5-FU) was significantly superior to either monotherapy (p<0.01). In particular, the growth of the Col-1 cells was completely inhibited by the combination of S-1 and bevacizumab. No toxic mortalities and no significant difference in the body weight changes of the animals treated with S-1 combined with the targeted agents or with the mono-therapies were observed; therefore, the treatments appeared to be well-tolerated. Our preclinical findings indicate that the combination therapies of S-1 and targeted agents are promising treatment options.
Figures
References
-
- Popov I, Milicević M, Radosević-Jelić LJ. The addition of bevacizumab to fluoropyrimidine, irinotecan and oxaliplatin-based therapy improves survival for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC): combined analysis of efficacy. Acta Chir Iugosl. 2008;55:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Meyerhardt JA, Stuart K, Fuchs CS, Zhu AX, Earle CC, Bhargava P, Blaszkowsky L, Enzinger P, Mayer RJ, Battu S, et al. Phase II study of FOLFOX, bevacizumab and erlotinib as first-line therapy for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:1185–1189. - PubMed
-
- Boccia RV, Cosgriff TM, Headley DL, Badarinath S, Dakhil SR. A phase II trial of FOLFOX6 and cetuximab in the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2010;9:102–107. - PubMed
-
- Dal Lago L, D’Hondt V, Awada A. Selected combination therapy with sorafenib: a review of clinical data and perspectives in advanced solid tumors. Oncologist. 2008;13:845–858. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
