Synergistic impact of Lactobacillus fermentum, Lactobacillus plantarum and vincristine on 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colorectal carcinogenesis in mice
- PMID: 22970015
- PMCID: PMC3438560
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2012.536
Synergistic impact of Lactobacillus fermentum, Lactobacillus plantarum and vincristine on 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colorectal carcinogenesis in mice
Abstract
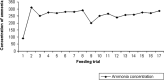
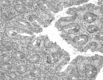
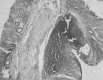
Lactobacillus sp. is the most dominant probiotic strain of bacteria. Evidence indicates that the consumption of Lactobacillus sp. reduces the risk of colorectal cancer in animal models. The present study was carried out to determine whether administration of Lactobacillus fermentum/ Lactobacillus plantarum alone or in combination with vincristine have a synergistic impact on the control of colorectal cancer in an animal model. Mice with 1,2 dimethylhydrazine (DMH) hydrochloride-induced colon cancer were fed with L. fermentum and L. plantarum isolated along with vincristine. An increase in body weight, a decrease in ammonia concentration, a decrease in β glucosidase and β glucuronidase enzyme activity and a reduction in the number of crypts in the mice in the pre-carcinogen-induced group was noted when compared to these variables in the post-carcinogen-induced group. The body weight of the mice fed L. fermentum along with vincristine was increased (6.5 g), and was found to be 3.5 times higher compared to that of the control. A marked decrease in the ammonia concentration (240 mg), and β glucosidase (0.0023 IU) and β glucopyranose enzyme activity (0.0027 IU) was observed; 22.59% less ammonia concentration, 73.26% less β glucosidase activity and 56.46% less β glucuronidase enzyme activity was noted when compared to the control. A significant reduction in the number of aberrant crypt foci (ACF) (90%) was observed when compared to the control. Maximum protection was observed in the mice fed the probiotics and vincristine prior to cancer induction. Among the different dietary combinations tested in the present study, L. fermentum and vincristine showed a more extensive reduction in ammonia concentration, β glucosidase, β glucuronidase activity and the number of ACF.
Figures


References
-
- Jacela JY, DeRouchey JM, Tokach MD, et al. Feed additives for Swine: fact sheets – prebiotics and probiotics, and phytogenetics. J Swine Health Prod. 2010;18:132–136.
-
- Tomasik PJ, Tomasik P. Probiotics and prebiotics. Cereal Chem. 2003;80:113–117.
-
- Vanderhoof JA. Probiotics: future directions. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;73:1152–1155. - PubMed
-
- Harish K, Varghese T. Probiotics in humans – evidence based review. Calicut Med J. 2006;4:211–223.
-
- Jiang T, Savaiano DA. In vitro lactose fermentation by human colonic bacteria is modified by Lactobacillus acidophilus supplementation. J Nutr. 1997;127:1489–1495. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
