Microbial diversity and potential pathogens in ornamental fish aquarium water
- PMID: 22970112
- PMCID: PMC3435374
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039971
Microbial diversity and potential pathogens in ornamental fish aquarium water
Abstract
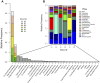
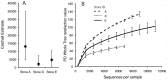
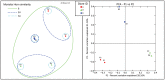
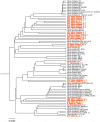
Ornamental fishes are among the most popular and fastest growing categories of pets in the United States (U.S.). The global scope and scale of the ornamental fish trade and growing popularity of pet fish in the U.S. are strong indicators of the myriad economic and social benefits the pet industry provides. Relatively little is known about the microbial communities associated with these ornamental fishes or the aquarium water in which they are transported and housed. Using conventional molecular approaches and next generation high-throughput amplicon sequencing of 16S ribosomal RNA gene hypervariable regions, we characterized the bacterial community of aquarium water containing common goldfish (Carassius auratus) and Chinese algae eaters (Gyrinocheilus aymonieri) purchased from seven pet/aquarium shops in Rhode Island and identified the presence of potential pathogens. Our survey identified a total of 30 phyla, the most common being Proteobacteria (52%), Bacteroidetes (18%) and Planctomycetes (6%), with the top four phyla representing >80% of all sequences. Sequences from our water samples were most closely related to eleven bacterial species that have the potential to cause disease in fishes, humans and other species: Coxiella burnetii, Flavobacterium columnare, Legionella birminghamensis, L. pneumophila, Vibrio cholerae, V. mimicus. V. vulnificus, Aeromonas schubertii, A. veronii, A. hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides. Our results, combined with evidence from the literature, suggest aquarium tank water harboring ornamental fish are an understudied source for novel microbial communities and pathogens that pose potential risks to the pet industry, fishes in trade, humans and other species.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- American Pet Products Association website. Available: http://www.americanpetproducts.org/pubs_survey.asp. Accessed 2011 Jan 15.
-
- Smith KF, Behrens MD, Max LM, Daszak P (2008) U.S. drowning in unidentified fishes: Scope, implications, and regulation of live fish import. Conserv Letters 1: 103–109.
-
- Smith KF, Behrens M, Schloegel LM, Marano N, Burgiel S, et al. (2009) Reducing the risks of the wildlife trade. Science 324: 594–595. - PubMed
-
- Raja K, Fernando O, Thavasi R, Jayalaksmi S, Balasubramanian T (2006) Diversity of bacterial populations in recirculating marine aquarium with different marine ornamental fishes. Res J Microbiol 5: 448–452.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

