Diversity and complexity in chromatin recognition by TFII-I transcription factors in pluripotent embryonic stem cells and embryonic tissues
- PMID: 22970219
- PMCID: PMC3438194
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044443
Diversity and complexity in chromatin recognition by TFII-I transcription factors in pluripotent embryonic stem cells and embryonic tissues
Abstract
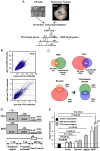
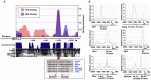
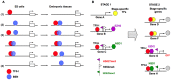
GTF2I and GTF2IRD1 encode a family of closely related transcription factors TFII-I and BEN critical in embryonic development. Both genes are deleted in Williams-Beuren syndrome, a complex genetic disorder associated with neurocognitive, craniofacial, dental and skeletal abnormalities. Although genome-wide promoter analysis has revealed the existence of multiple TFII-I binding sites in embryonic stem cells (ESCs), there was no correlation between TFII-I occupancy and gene expression. Surprisingly, TFII-I recognizes the promoter sequences enriched for H3K4me3/K27me3 bivalent domain, an epigenetic signature of developmentally important genes. Moreover, we discovered significant differences in the association between TFII-I and BEN with the cis-regulatory elements in ESCs and embryonic craniofacial tissues. Our data indicate that in embryonic tissues BEN, but not the highly homologous TFII-I, is primarily recruited to target gene promoters. We propose a "feed-forward model" of gene regulation to explain the specificity of promoter recognition by TFII-I factors in eukaryotic cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Epigenetic modulation by TFII-I during embryonic stem cell differentiation.J Cell Biochem. 2012 Oct;113(10):3056-60. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24202. J Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22628223 Review.
-
TFII-I and AP2α Co-Occupy the Promoters of Key Regulatory Genes Associated with Craniofacial Development.Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2018 Jul;55(6):865-870. doi: 10.1597/15-214. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2018. PMID: 28085512
-
ChIP-Chip Identifies SEC23A, CFDP1, and NSD1 as TFII-I Target Genes in Human Neural Crest Progenitor Cells.Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2013 May;50(3):347-50. doi: 10.1597/12-069. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2013. PMID: 23145914
-
Essential functions of the Williams-Beuren syndrome-associated TFII-I genes in embryonic development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jan 6;106(1):181-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811531106. Epub 2008 Dec 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19109438 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription regulation and chromatin structure in the pluripotent ground state.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Mar;1839(3):129-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.09.005. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24096207 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation and Elongation by Transcription Factor TFII-I.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 13;8:681550. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.681550. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34055891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal Gtf2i deletion alters mitochondrial and autophagic properties.Commun Biol. 2023 Dec 14;6(1):1269. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05612-5. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 38097729 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of seven in absentia homolog-1 in ethanol-induced apoptosis in neural crest cells.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2014 Nov-Dec;46:26-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2014. PMID: 25193017 Free PMC article.
-
Symmetrical Dose-Dependent DNA-Methylation Profiles in Children with Deletion or Duplication of 7q11.23.Am J Hum Genet. 2015 Aug 6;97(2):216-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.05.019. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Am J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 26166478 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of Gtf2i and Gtf2ird1 in the developing brain: transcription, DNA binding and long-term behavioral consequences.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Jun 3;29(9):1498-1519. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa070. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 32313931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayarsaihan D, Bitchevaia NK, Enkhmandakh B, Tussie-Luna MI, Leckman JF, et al. (2003) Expression of BEN, a member of TFII-I family of transcription factors, during mouse pre- and postimplantation development. Gene Expres Patterns 3: 577–587. - PubMed
-
- Enkhmandakh B, Bitchevaia N, Ruddle F, Bayarsaihan D (2004) The early embryonic expression of TFII-I during mouse preimplantation development. Gene Expr Patterns 4: 25–28. - PubMed
-
- Chimge N, Makeyev AV, Waigel SJ, Enkhmandakh B, Bayarsaihan D (2012) PI3K/Akt-dependent functions of TFII-I transcription factors in mouse embryonic stem cells. J Cell Biochem 113: 1122–1131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

