SU5416, a VEGF receptor inhibitor and ligand of the AHR, represents a new alternative for immunomodulation
- PMID: 22970246
- PMCID: PMC3435281
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044547
SU5416, a VEGF receptor inhibitor and ligand of the AHR, represents a new alternative for immunomodulation
Abstract
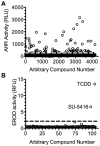
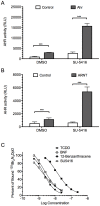
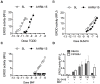
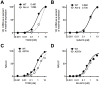
The experimental compound SU5416 went as far as Phase III clinical trials as an anticancer agent, putatively because of its activity as a VEGFR-2 inhibitor, but showed poor results. Here, we show that SU5416 is also an aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) agonist with unique properties. Like TCDD, SU5416 favors induction of indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO) in immunologically relevant populations such as dendritic cells in an AHR-dependent manner, leading to generation of regulatory T-cells in vitro. These characteristics lead us to suggest that SU5416 may be an ideal clinical agent for treatment of autoimmune diseases and prevention of transplant rejection, two areas where regulatory ligands of the AHR have shown promise. At the same time, AHR agonism might represent a poor characteristic for an anticancer drug, as regulatory T-cells can inhibit clearance of cancer cells, and activation of the AHR can lead to upregulation of xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes that might influence the half-lives of co-administered chemotherapeutic agents. Not only does SU5416 activate the human AHR with a potency approaching 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, but it also activates polymorphic murine receptor isoforms (encoded by the Ahr(d) and Ahr(b1) alleles) with similar potency, a finding that has rarely been described and may have implications in identifying true endogenous ligands of this receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Amacher DE (2010) The effects of cytochrome P450 induction by xenobiotics on endobiotic metabolism in pre-clinical safety studies. Toxicol Mech Methods 20: 159–166. - PubMed
-
- Knerr S, Schrenk D (2006) Carcinogenicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in experimental models. Mol Nutr Food Res 50: 897–907. - PubMed
-
- Thackaberry EA, Gabaldon DM, Walker MK, Smith SM (2002) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor null mice develop cardiac hypertrophy and increased hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in the absence of cardiac hypoxia. Cardiovasc Toxicol 2: 263–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

