Intracellular Delivery of siRNA by Polycationic Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles
- PMID: 22970377
- PMCID: PMC3437298
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/218940
Intracellular Delivery of siRNA by Polycationic Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles
Abstract
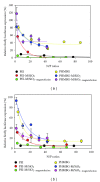
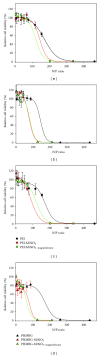
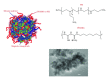
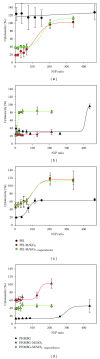
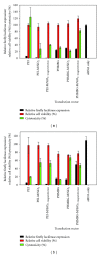
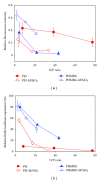
The siRNA transfection efficiency of nanoparticles (NPs), composed of a superparamagnetic iron oxide core modified with polycationic polymers (poly(hexamethylene biguanide) or branched polyethyleneimine), were studied in CHO-K1 and HeLa cell lines. Both NPs demonstrated to be good siRNA transfection vehicles, but unmodified branched polyethyleneimine (25 kD) was superior on both cell lines. However, application of an external magnetic field during transfection (magnetofection) increased the efficiency of the superparamagnetic NPs. Furthermore, our results reveal that these NPs are less toxic towards CHO-K1 cell lines than the unmodified polycationic-branched polyethyleneimine (PEI). In general, the external magnetic field did not alter the cell's viability nor it disrupted the cell membranes, except for the poly(hexamethylene biguanide)-modified NP, where it was observed that in CHO-K1 cells application of the external magnetic field promoted membrane damage. This paper presents new polycationic superparamagnetic NPs as promising transfection vehicles for siRNA and demonstrates the advantages of magnetofection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of PEGylated Magnetic PLGA-PEI Nanoparticles on Primary Hippocampal Neurons: Reduced Nanoneurotoxicity and Enhanced Transfection Efficiency with Magnetofection.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Oct 16;11(41):38190-38204. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b15014. Epub 2019 Oct 4. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 31550131
-
Improving Magnetofection of Magnetic Polyethylenimine Nanoparticles into MG-63 Osteoblasts Using a Novel Uniform Magnetic Field.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2019 Mar 12;14(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s11671-019-2882-5. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2019. PMID: 30874913 Free PMC article.
-
Silica nanoparticles and polyethyleneimine (PEI)-mediated functionalization: a new method of PEI covalent attachment for siRNA delivery applications.Bioconjug Chem. 2013 Dec 18;24(12):2076-87. doi: 10.1021/bc4004316. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Bioconjug Chem. 2013. PMID: 24180511
-
Polyethyleneimine-associated polycaprolactone-Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a gene delivery vector.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017 Jan;105(1):145-154. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33519. Epub 2015 Oct 6. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017. PMID: 26443109
-
Nonviral Locally Injected Magnetic Vectors for In Vivo Gene Delivery: A Review of Studies on Magnetofection.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Apr 22;11(5):1078. doi: 10.3390/nano11051078. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogen- and Host-Directed Antileishmanial Effects Mediated by Polyhexanide (PHMB).PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015 Oct 2;9(10):e0004041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004041. eCollection 2015. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015. PMID: 26431058 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of siRNA delivery enhancers by a chemical library screen.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Sep 18;43(16):7984-8001. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv762. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26220182 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic micelles for DNA delivery to rat brains after mild traumatic brain injury.Nanomedicine. 2014 Oct;10(7):1539-48. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24486465 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Applications of Targeted Nanomaterials.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Mar 17;17(3):379. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17030379. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40143042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of ferriferous oxide modified by chitosan in gene delivery.J Drug Deliv. 2012;2012:920764. doi: 10.1155/2012/920764. Epub 2012 Dec 27. J Drug Deliv. 2012. PMID: 23326667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jones SW, de Souza PM, Lindsay MMA. siRNA for gene silencing: a route to drug target discovery. Current Opinion in Pharmacology. 2004;4(5):522–527. - PubMed
-
- Fabani MM, Turner JJ, Gait MJ. Oligonucleotide analogs as antiviral agents. Current Opinion in Molecular Therapeutics. 2006;8(2):108–114. - PubMed
-
- Masiero M, Nardo G, Indraccolo S, Favaro E. RNA interference: implications for cancer treatment. Molecular Aspects of Medicine. 2007;28(1):143–166. - PubMed
-
- Biswal BK, Debata NB, Verma RS. Development of a targeted siRNA delivery system using FOL-PEG-PEI conjugate. Molecular Biology Reports. 2010;37(6):2919–2926. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

