Salicylanilide inhibitors of Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 22970937
- PMCID: PMC3498903
- DOI: 10.1021/jm3007596
Salicylanilide inhibitors of Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) is an apicomplexan parasite that can cause eye disease, brain disease, and death, especially in congenitally infected and immune-compromised people. Novel medicines effective against both active and latent forms of the parasite are greatly needed. The current study focused on the discovery of such medicines by exploring a family of potential inhibitors whose antiapicomplexan activity has not been previously reported. Initial screening efforts revealed that niclosamide, a drug approved for anthelmintic use, possessed promising activity in vitro against T. gondii. This observation inspired the evaluation of the activity of a series of salicylanilides and derivatives. Several inhibitors with activities in the nanomolar range with no appreciable in vitro toxicity to human cells were identified. An initial structure-activity relationship was explored. Four compounds were selected for evaluation in an in vivo model of infection, and two derivatives with potentially enhanced pharmacological parameters demonstrated the best activity profiles.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

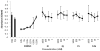
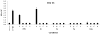
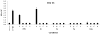
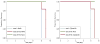



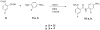
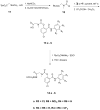
References
-
- McLeod R, Boyer K, Karrison T, Kasza K, Swisher C, Roizen N, Jalbrzikowski J, Remington J, Heydemann P, Noble AG, Mets M, Holfels E, Withers S’, Latkany P, Meier P. Outcome of treatment for congenital toxoplasmosis, 1981–2004: the National Collaborative Chicago-Based, Congenital Toxoplasmosis Study. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:1383–1394. - PubMed
-
- Roizen N, Kasza K, Karrison T, Mets M, Noble AG, Boyer K, Swisher C, Meier P, Remington J, Jalbrzikowski J, McLeod R, Kipp M, Rabiah P, Chamot D, Estes R, Cezar S, Mack D, Pfiffner L, Stein M, Danis B, Patel D, Hopkins J, Holfels E, Stein L, Withers S, Cameron A, Perkins J, Heydemann P. Impact of visual impairment on measures of cognitive function for children with congenital toxoplasmosis: implications for compensatory intervention strategies. Pediatrics. 2006;118:e379–390. - PubMed
-
- McLeod R, Khan AR, Noble GA, Latkany P, Jalbrzikowski J, Boyer K. Severe sulfadiazine hypersensitivity in a child with reactivated congenital toxoplasmic chorioretinitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:270–272. - PubMed
-
-
NDA #018669 (Bayer)
-
-
- Weinbach EC, Garbus J. Mechanism of action of reagents that uncouple oxidative phosphorylation. Nature. 1969;221:1016–1018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

