Doppler resistive index to reflect regulation of renal vascular tone during sepsis and acute kidney injury
- PMID: 22971333
- PMCID: PMC3682260
- DOI: 10.1186/cc11517
Doppler resistive index to reflect regulation of renal vascular tone during sepsis and acute kidney injury
Abstract
Introduction: Renal resistive index (RI), determined by Doppler ultrasonography, directly reveals and quantifies modifications in renal vascular resistance. The aim of this study was to evaluate if mean arterial pressure (MAP) is determinant of renal RI in septic, critically ill patients suffering or not from acute kidney injury (AKI).
Methods: This prospective observational study included 96 patients. AKI was defined according to RIFLE criteria and transient or persistent AKI according to renal recovery within 3 days.
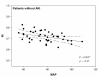
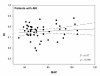
Results: Median renal RIs were 0.72 (0.68-0.75) in patients without AKI and 0.76 (0.72-0.80) in patients with AKI (P = 0.001). RIs were 0.75 (0.72-0.79) in transient AKI and 0.77 (0.70-0.80) in persistent AKI (P = 0.84). RI did not differ in patients given norepinephrine infusion and was not correlated with norepinephrine dose. RI was correlated with MAP (ρ = -0.47; P = 0.002), PaO2/FiO2 ratio (ρ = -0.33; P = 0.04) and age (ρ = 0.35; P = 0.015) only in patients without AKI.
Conclusions: A poor correlation between renal RI and MAP, age, or PaO2/FiO2 ratio was found in septic and critically ill patients without AKI compared to patients with AKI. These findings suggest that determinants of RI are multiple. Renal circulatory response to sepsis estimated by Doppler ultrasonography cannot reliably be predicted simply from changes in systemic hemodynamics. As many factors influence its value, the interest in a single RI measurement at ICU admission to determine optimal MAP remains uncertain.
Figures
Comment in
-
Please don't call me RI anymore; I may not be the one you think I am!Crit Care. 2012 Nov 15;16(6):174. doi: 10.1186/cc11831. Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 23171782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, Ronco C. Beginning and Ending Supportive Therapy for the Kidney (BEST Kidney) Investigators. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;16:813–818. doi: 10.1001/jama.294.7.813. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Antonelli M, Azoulay E, Bonten M, Chastre J, Citerio G, Conti G, De Backer D, Gerlach H, Hedenstierna G, Joannidis M, Macrae D, Mancebo J, Maggiore SM, Mebazaa A, Preiser JC, Pugin J, Wernerman J, Zhang H. Year in review in Intensive Care Medicine 2010: I. Acute renal failure, outcome, risk assessment and ICU performance, sepsis, neuro intensive care and experimentals. Intensive Care Med. 2011;16:19–34. doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-2112-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

