RhoJ regulates melanoma chemoresistance by suppressing pathways that sense DNA damage
- PMID: 22971344
- PMCID: PMC3548429
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0775
RhoJ regulates melanoma chemoresistance by suppressing pathways that sense DNA damage
Abstract
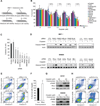
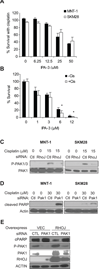
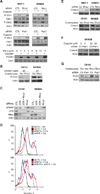
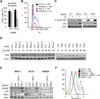
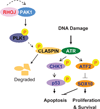
Melanomas resist conventional chemotherapeutics, in part, through intrinsic disrespect of apoptotic checkpoint activation. In this study, using an unbiased genome-wide RNA interference screen, we identified RhoJ and its effector PAK1, as key modulators of melanoma cell sensitivity to DNA damage. We find that RhoJ activates PAK1 in response to drug-induced DNA damage, which then uncouples ATR from its downstream effectors, ultimately resulting in a blunted DNA damage response (DDR). In addition, ATR suppression leads to the decreased phosphorylation of ATF2 and consequent increased expression of the melanocyte survival gene Sox10 resulting in a higher DDR threshold required to engage melanoma cell death. In the setting of normal melanocyte behavior, this regulatory relationship may facilitate appropriate epidermal melanization in response to UV-induced DNA damage. However, pathologic pathway activation during oncogenic transformation produces a tumor that is intrinsically resistant to chemotherapy and has the propensity to accumulate additional mutations. These findings identify DNA damage agents and pharmacologic inhibitors of RhoJ/PAK1 as novel synergistic agents that can be used to treat melanomas that are resistant to conventional chemotherapies.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
RhoJ modulates melanoma invasion by altering actin cytoskeletal dynamics.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013 Mar;26(2):218-25. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12058. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013. PMID: 23253891 Free PMC article.
-
RSK promotes G2 DNA damage checkpoint silencing and participates in melanoma chemoresistance.Oncogene. 2013 Sep 19;32(38):4480-9. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.472. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 23108403
-
The RhoJ-BAD signaling network: An Achilles' heel for BRAF mutant melanomas.PLoS Genet. 2017 Jul 28;13(7):e1006913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006913. eCollection 2017 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28753606 Free PMC article.
-
RhoJ: an emerging biomarker and target in cancer research and treatment.Cancer Gene Ther. 2024 Oct;31(10):1454-1464. doi: 10.1038/s41417-024-00792-6. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38858534 Review.
-
Drug resistance in human melanoma: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities.Onkologie. 2003 Dec;26(6):581-7. doi: 10.1159/000074156. Onkologie. 2003. PMID: 14709935 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual Modal Imaging-Guided Drug Delivery System for Combined Chemo-Photothermal Melanoma Therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 May 18;16:3457-3472. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S306269. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34045853 Free PMC article.
-
MORC2, a novel oncogene, is upregulated in liver cancer and contributes to proliferation, metastasis and chemoresistance.Int J Oncol. 2018 Jul;53(1):59-72. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4333. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29620211 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Histone H4T80 Triggers DNA Damage Checkpoint Recovery.Mol Cell. 2018 Nov 15;72(4):625-635.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.09.023. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30454561 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering potential diagnostic and pathophysiological roles of α-synuclein and DJ-1 in melanoma.Cancer Med. 2024 Jan;13(1):e6900. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6900. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38189631 Free PMC article.
-
TCL/RhoJ Plasma Membrane Localization and Nucleotide Exchange Is Coordinately Regulated by Amino Acids within the N Terminus and a Distal Loop Region.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 4;291(45):23604-23617. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.750026. Epub 2016 Sep 22. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27660391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsao H, Atkins MB, Sober AJ. Management of cutaneous melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:998–1012. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury PA, Middleton MR. DNA repair pathways in drug resistance in melanoma. Anticancer Drugs. 2004;15:421–426. - PubMed
-
- Solit DB, Rosen N. Resistance to BRAF inhibition in melanomas. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:772–774. - PubMed
-
- Soengas MS, Lowe SW. Apoptosis and melanoma chemoresistance. Oncogene. 2003;22:3138–3151. - PubMed
-
- Lee JT, Herlyn M. MEK'ing the most of p53 reactivation therapy in melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:263–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

