Uremia causes premature ageing of the T cell compartment in end-stage renal disease patients
- PMID: 22971545
- PMCID: PMC3482595
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4933-9-19
Uremia causes premature ageing of the T cell compartment in end-stage renal disease patients
Abstract
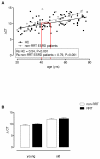
Background: End-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients treated with renal replacement therapy (RRT) have premature immunologically aged T cells which may underlie uremia-associated immune dysfunction. The aim of this study was to investigate whether uremia was able to induce premature ageing of the T cell compartment. For this purpose, we examined the degree of premature immunological T cell ageing by examining the T cell differentiation status, thymic output via T cell receptor excision circle (TREC) content and proliferative history via relative telomere length in ESRD patients not on RRT.
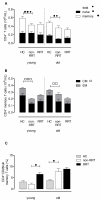
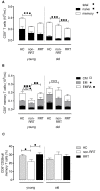
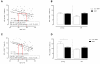
Results: Compared to healthy controls, these patients already had a lower TREC content and an increased T cell differentiation accompanied by shorter telomeres. RRT was able to enhance CD8+ T cell differentiation and to reduce CD8+ T cell telomere length in young dialysis patients. An increased differentiation status of memory CD4+ T cells was also noted in young dialysis patients.
Conclusion: Based on these results we can conclude that uremia already causes premature immunological ageing of the T cell system and RRT further increases immunological ageing of the CD8+ T cell compartment in particular in young ESRD patients.
Figures
References
-
- Litjens NH, van Druningen CJ, Betjes MG. Progressive loss of renal function is associated with activation and depletion of naive T lymphocytes. ClinImmunol. 2006;118:83–91. - PubMed
-
- Vanholder R, Ringoir S. Infectious morbidity and defects of phagocytic function in end-stage renal disease: a review. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1993;3:1541–1554. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

