Novel coumarin derivatives containing 1,2,4-triazole, 4,5-dicyanoimidazole and purine moieties: synthesis and evaluation of their cytostatic activity
- PMID: 22971585
- PMCID: PMC6268888
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules170911010
Novel coumarin derivatives containing 1,2,4-triazole, 4,5-dicyanoimidazole and purine moieties: synthesis and evaluation of their cytostatic activity
Abstract
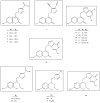
We report here on the synthesis and in vitro anti-tumor effects of a series of novel 1,2,4-triazole (compounds 3-6), 4,5-dicyanoimidazole (compound 7), and purine (compounds 8-13) coumarin derivatives and their acyclic nucleoside analogues 14-18. Structures of novel compounds 3-18 were deduced from their (1)H- and (13)C-NMR and corresponding mass spectra. Results of anti-proliferative assays performed on a panel of selected human tumor cell lines revealed that compound 6 had moderate cytostatic activity against the HeLa cell line (IC(50) = 35 µM), whereas compound 10 showed moderate activity against the HeLa (IC(50) = 33 µM), HepG2 (IC(50) = 25 µM) and SW620 (IC(50) = 35 µM) cell lines. These compounds showed no cytotoxic effects on normal (diploid) human fibroblasts.
Figures

References
-
- Harvey R.G., Cortez C., Ananthanarayan T.P., Schmolka S. A new coumarin synthesis and its utilization for the synthesis of polycyclic coumarin compounds with anticarcinogenic properties. J. Org. Chem. 1988;53:3936–3943.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

